Case Summary: Forever 21 Chapter 11
Forever 21 has filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy, citing competition from online retailers such as Shein and Temu, inflation, and shifting customer preferences, with plans for an expedited store liquidation and potential asset sale.

Business Description
F21 OpCo, LLC, along with its affiliated Debtors⁽¹⁾ (collectively, “Forever 21” or the “Company”), is a U.S.-based fast-fashion retailer known for trendy, affordable apparel and accessories. Originally founded in 1984 by Do Won and Jin Sook Chang, Forever 21 gained prominence through large-format stores situated in high-traffic malls, targeting budget-conscious young consumers.
- Store Footprint & E-Commerce: As of the Petition Date, Forever 21 operated approximately 354 leased U.S. stores—most in shopping malls—and maintained an e-commerce platform launched in the early 2000s.
- Licensing & Ownership Structure: A subsidiary of Authentic Brands Group (“ABG”) holds the Forever 21 intellectual property, licensing it to the Debtors for merchandise sales in specified regions and product categories. Operationally, Forever 21 falls under SPARC Group Holdings LLC (“SPARC”), which was majority-owned by Simon Property Group and ABG until SPARC’s acquisition by JC Penney in December 2024. The Company now operates within Catalyst Brands, a retail umbrella entity formed post-acquisition.
Forever21 filed for Chapter 11 protection on Mar. 16 in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the District of Delaware. As of the Petition Date, the Debtors reported $100 million to $500 million in assets and $1 billion to $10 billion in liabilities.
⁽¹⁾ F21 Puerto Rico, LLC and F21 GiftCo Management, LLC.
Corporate History
Forever 21 expanded aggressively from a single 900-square-foot storefront in Los Angeles to a global fast-fashion powerhouse. By its peak in the mid-2010s, the Company employed over 43,000 people, generated more than $4 billion in annual sales, and operated hundreds of stores worldwide.
- 2019 Bankruptcy: Faced with sales declines, rent obligations on oversized stores, and underperforming international expansions, the then–family-owned business (“Old F21”) filed for Chapter 11 in September 2019. After closing most international locations, the Company was sold in February 2020 to a joint venture of Simon Property Group, Brookfield Property Partners, and ABG for $81 million.
- Transition to SPARC: Following the 2020 reorganization, Brookfield exited its stake, and SPARC assumed control of U.S. operations. The brand initially saw a post-pandemic rebound, with FY 2021 revenue of $2 billion and EBITDA of $165 million. However, mounting macroeconomic and competitive pressures eroded profitability from 2022 onward.
- Catalyst Brands Formation: In December 2024, JC Penney acquired SPARC, rolling Forever 21 and several other banners into Catalyst Brands. Despite a broader portfolio of 1,800 stores and 60,000 employees, Catalyst soon announced its intent to explore “strategic options” for Forever 21, ultimately paving the way for the Company’s second Chapter 11 filing.
Organizational Structure
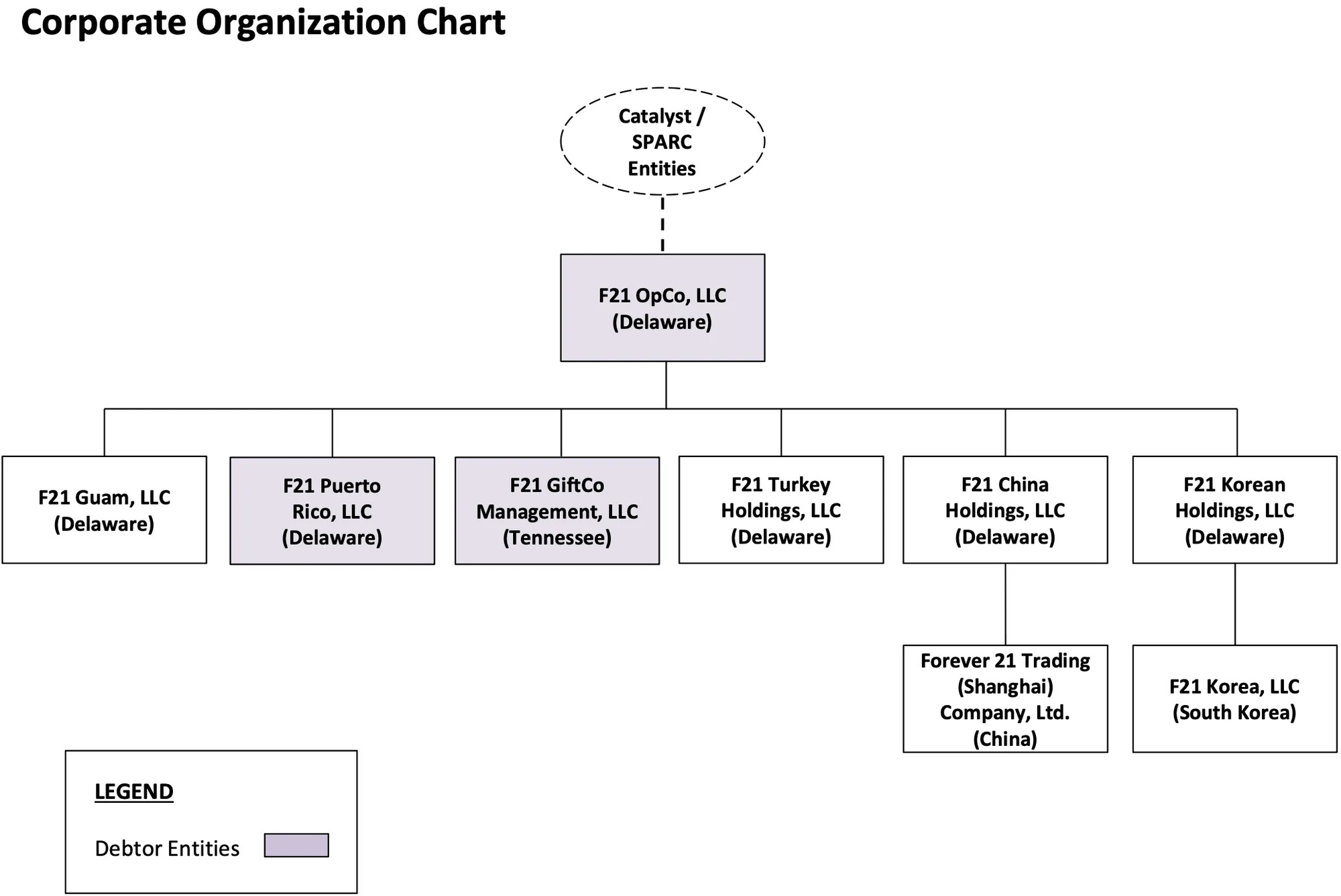
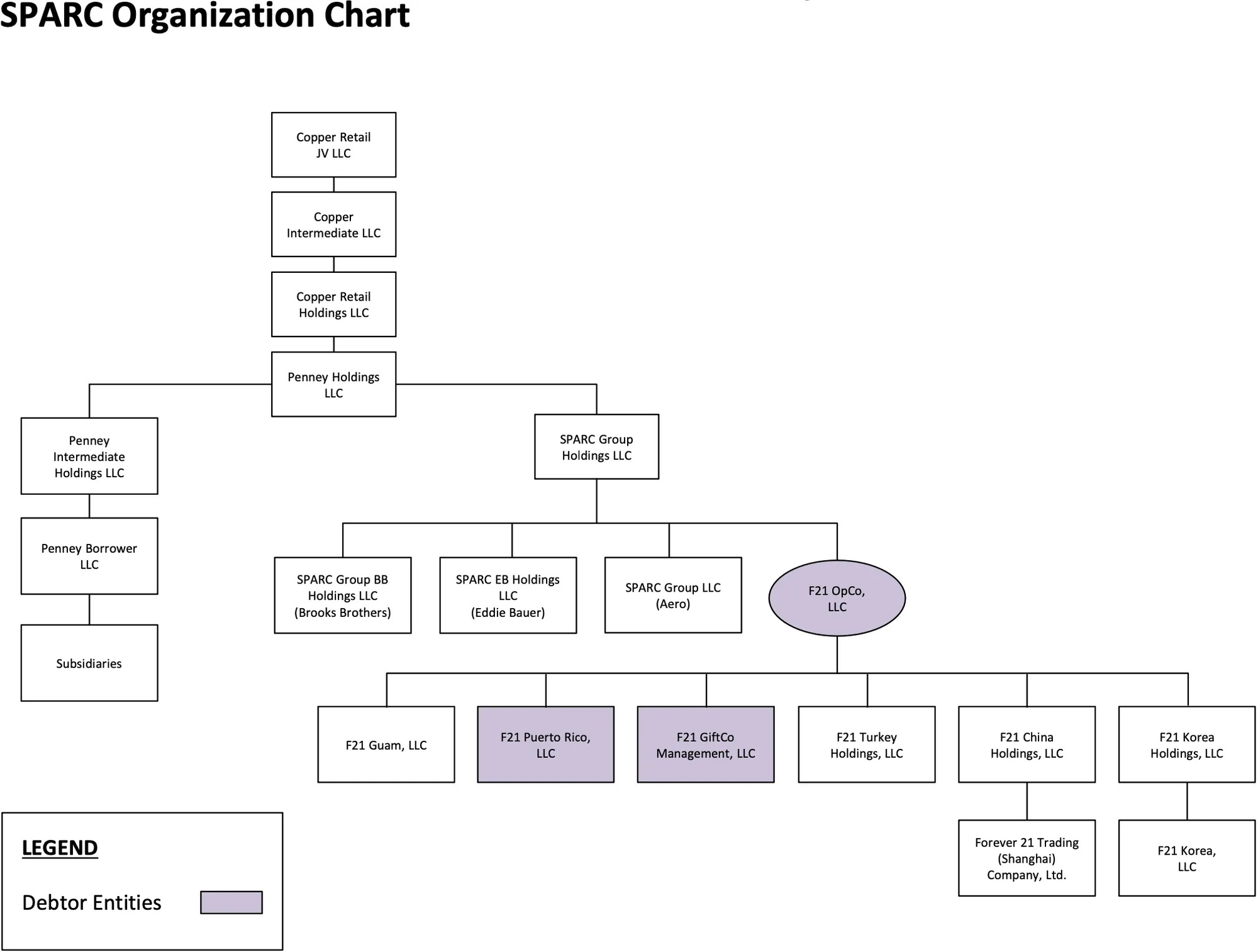
Operations Overview
Forever 21’s domestic footprint and supply chain—once key drivers of growth—have become increasingly burdensome amid shifting consumer trends and online competition.
- Retail Footprint: Historically, Forever 21 leased large-format spaces averaging 38,000 square feet in malls nationwide. As of early 2025, the Company operated 354 U.S. stores from 78 unique landlords, including Simon Property Group (27% of leases) and Brookfield Property Partners (19%).
- E-Commerce Platform: Despite launching Forever21.com nearly two decades ago, the Company lagged behind digital-native rivals. An attempted platform upgrade in 2021 reportedly caused significant online checkout disruptions, contributing to lost revenue and diminishing Forever 21’s ability to compete with ultra-fast-fashion e-tailers.
- Supply Chain & Distribution: Merchandise is sourced from an extensive network of foreign vendors. A 656,000-square-foot distribution center in Perris, CA, managed by third-party provider Maersk, handles most domestic fulfillment. Rising freight costs, wage inflation, and extended lead times contrasted sharply with the rapid “on-demand” supply models of online disruptors like Shein and Temu.
- Workforce Overview: As of the Petition Date, the Debtors employ approximately 1,750 full-time employees, 7,190 part-time employees, and roughly 320 seasonal employees. The Company implemented a Store Level Retention Program covering approximately 1,360 store-level employees to maintain adequate staffing throughout the liquidation process.
Prepetition Obligations
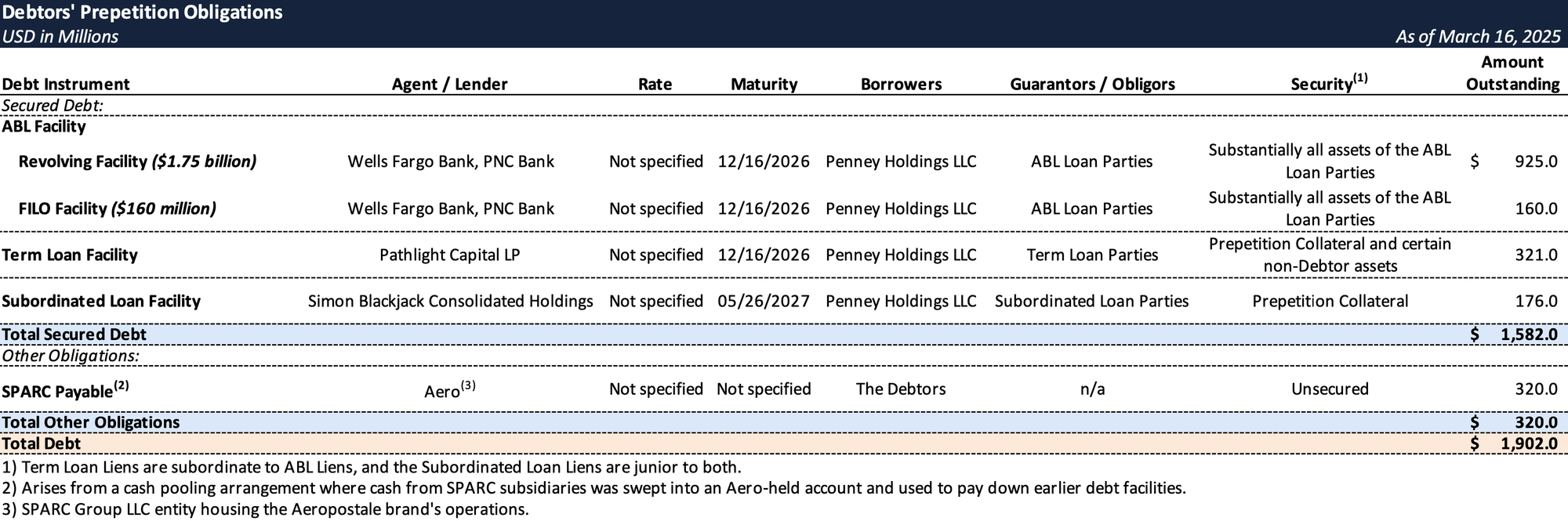
Top Unsecured Claims
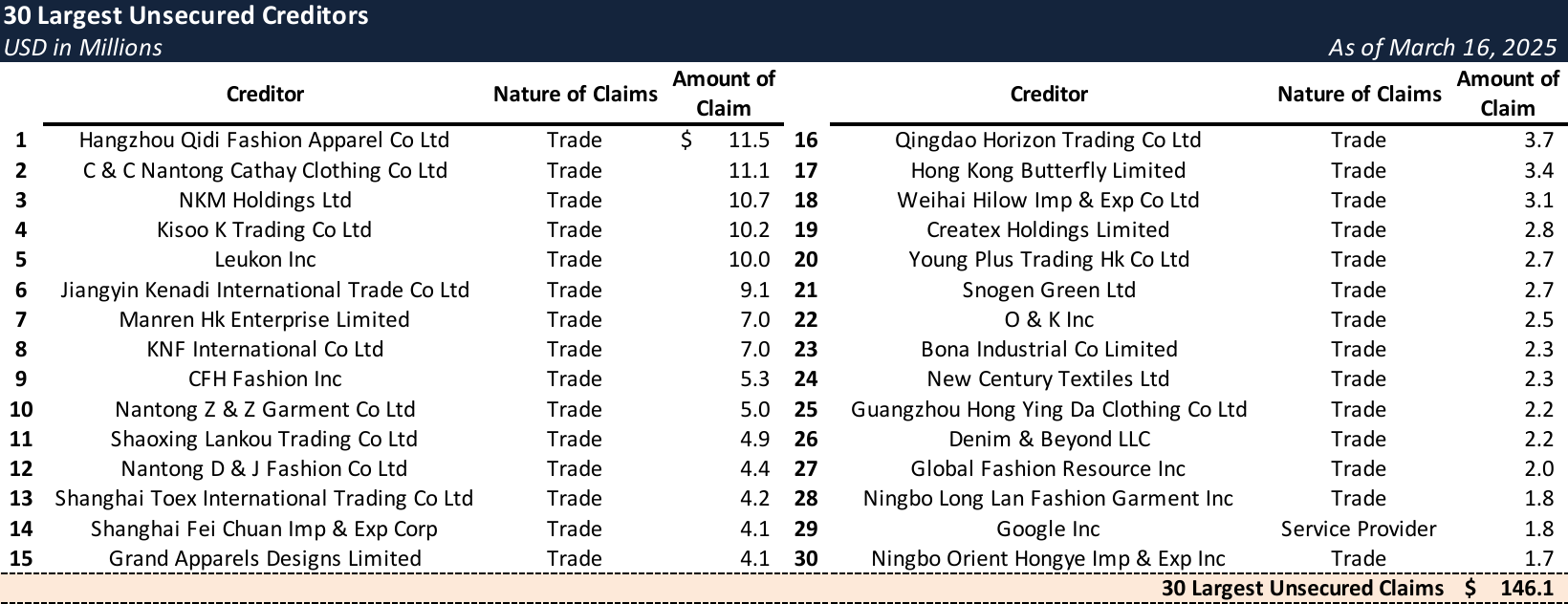
Events Leading to Bankruptcy
Macroeconomic Pressures & Competitive Challenges
Following the 2019 restructuring, Forever 21 briefly stabilized but soon confronted multiple headwinds:
- Inflationary Pressures: Surging costs of labor, transportation, and inventory from 2021 onward squeezed margins.
- De Minimis Exemption: Foreign-based fast-fashion platforms—most notably Shein and Temu—leveraged a U.S. duty exemption for direct-to-consumer shipments under $800, enabling them to undercut domestic retailers.
- Declining Mall Traffic & Online Shift: Persistent shifts in consumer behavior away from traditional malls further eroded store sales. The Company’s late and sometimes problematic e-commerce upgrades could not offset shrinking in-store foot traffic.
Operational Cost Reduction Efforts
In response, the Company pursued aggressive cost-saving measures:
- Renegotiated leases and licensing fees, reducing expenses by over $50 million.
- Closed 34 underperforming stores in 2024, hiring Hilco Merchant Resources to manage liquidation efforts.
- Secured significant rent concessions from key landlords and a 50% reduction in ABG licensing fees.
Despite these measures, Forever 21 posted more than $400 million in cumulative losses over the past three fiscal years and anticipated an additional $180 million EBITDA loss through 2025.
Exploration of Strategic Alternatives
Facing intensifying losses, Forever 21:
- Conducted informal sale discussions in 2024, but no transactions emerged.
- Retained Young Conaway, Paul Weiss, and BRG in January 2025 to assess restructuring pathways.
- Established an independent Board of Managers (including restructuring professionals) to supervise contingency planning.
When no actionable M&A proposals materialized, the Debtors initiated a dual-track strategy—simultaneously closing stores and exploring a going-concern sale.
Store Closing Sales & Liquidation Process
In February 2025, Forever 21 launched store closing sales at 236 locations; by late February, all remaining stores had entered liquidation.
- A joint venture of Hilco, Gordon Brothers, and SB360 Capital Partners was chosen to maximize recovery on in-store inventory and fixtures, with sales slated to conclude by May 1, 2025.
- The swift timeline preserves optionality for a potential going-concern transaction, should a buyer emerge during the liquidation process.
Going Concern Sale & Chapter 11 Plan
To reach the widest pool of potential buyers, the Company retained SSG Capital Advisors, which contacted 217 parties—30 of whom signed confidentiality agreements. Although interest was expressed, no binding offers had emerged prepetition.
On March 16, 2025, Forever 21 filed for Chapter 11 in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the District of Delaware:
- Plan Support Agreement (PSA): The Debtors secured a PSA with key secured lenders, providing for consensual use of cash collateral to fund the case and outlining a structured wind-down.
- Distribution & Timeline: General unsecured creditors may receive up to 6% of distributable proceeds, despite being deeply out of the money based on projected recoveries. Key milestones include filing the plan and disclosure statement by March 26, 2025, and seeking confirmation by mid-June 2025.
Forever 21’s second Chapter 11 filing in six years highlights the ongoing upheaval within the fast-fashion and mall-based retail sectors. While liquidation of the U.S. store fleet is underway, the Debtors continue to market assets for a possible going-concern transaction. Nonetheless, the brand’s intellectual property remains with ABG and may be licensed anew, potentially preserving the Forever 21 name outside of bankruptcy even as the current operating entities wind down.
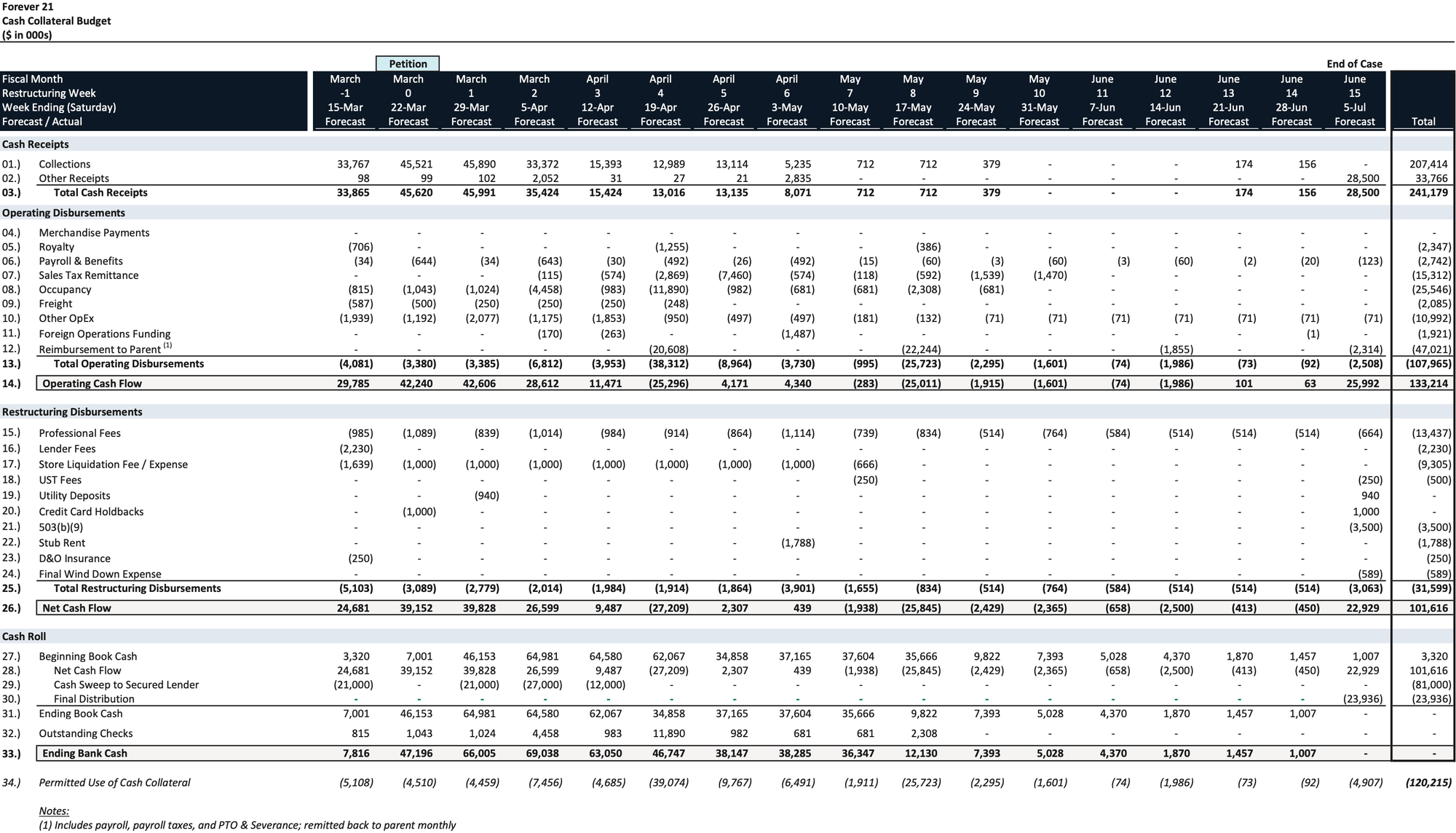
Cash Collateral Budget
Stay informed on every Chapter 11 bankruptcy case with liabilities exceeding $10 million. Subscribe for free to have our coverage delivered directly to your inbox, and explore our full archive of past summaries.
If you’re already a subscriber and would like to receive timely filing alerts, please reach out and we’ll add you to the distribution list.



