Case Summary: Global Clean Energy Chapter 11
Global Clean Energy has filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy amid construction delays, cost overruns, and protracted disputes involving its core Bakersfield renewable diesel refinery, aiming to restructure through a lender-backed plan.

Summary
- Vertically integrated renewable diesel producer Global Clean Energy Holdings files Chapter 11 (SDTX) citing liquidity crisis from Bakersfield refinery project failures.
- Filing driven by significant refinery delays, cost overruns, and protracted dispute with EPC contractor CTCI Americas, culminating in a ~$924.3M mechanic's lien.
- Enters bankruptcy with an RSA backed by key stakeholders: Ad Hoc Term Lenders (~96%), CTCI, and essential partner Vitol Americas.
- RSA underpins a pre-filed plan aimed at resolving CTCI disputes, deleveraging, and funded by DIP from RSA parties.
Business Description
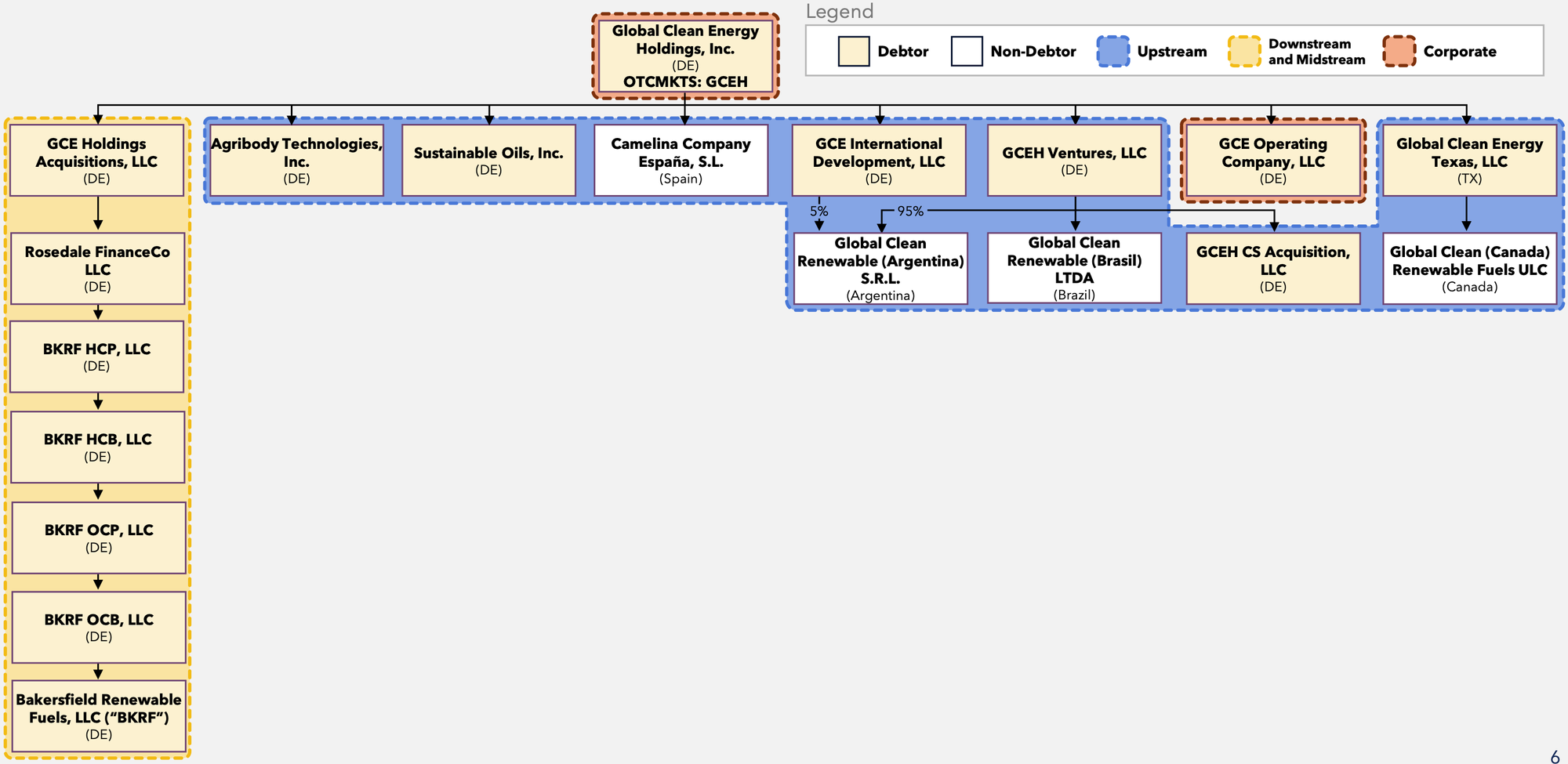
Headquartered in Bakersfield, CA, Global Clean Energy Holdings, Inc., along with its Debtor⁽¹⁾ and non-Debtor affiliates (collectively, "Global Clean Energy" or the "Company"), is a vertically integrated renewable energy company focused on producing sustainable, low-carbon renewable fuel designed as a direct replacement for petroleum-based diesel.
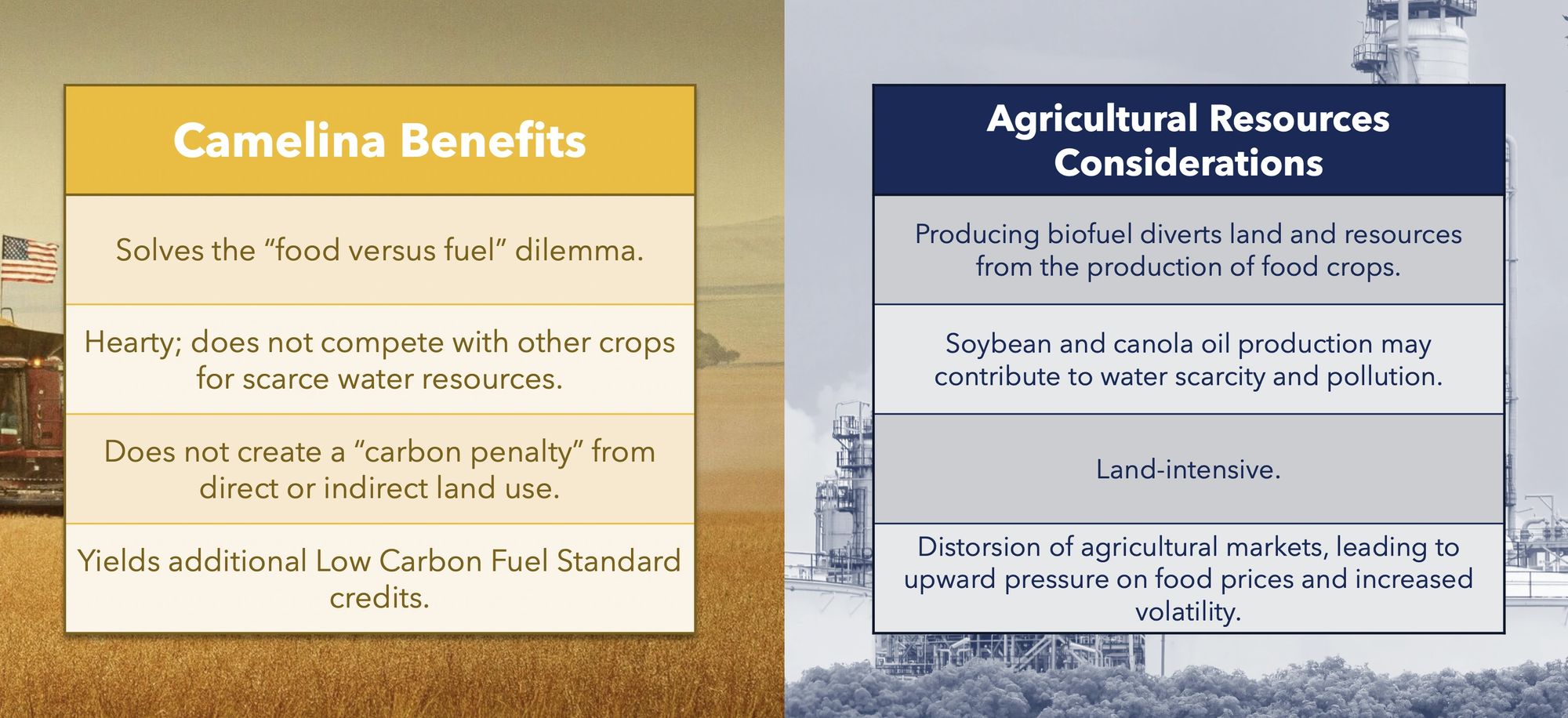
- The Company operates a unique "farm-to-fuel" model, encompassing the development and cultivation of proprietary feedstock, primarily Camelina sativa ("Camelina"), through to the refining and distribution of renewable diesel ("RD").
- This integrated approach aims to streamline operations, lower carbon emissions (potentially reducing greenhouse gas emissions by up to 85% compared to conventional diesel), and mitigate the "food versus fuel" conflict by utilizing non-sustenance crops like Camelina.
- Global Clean Energy employs over 150 people directly and manages contracts with hundreds of growers globally.
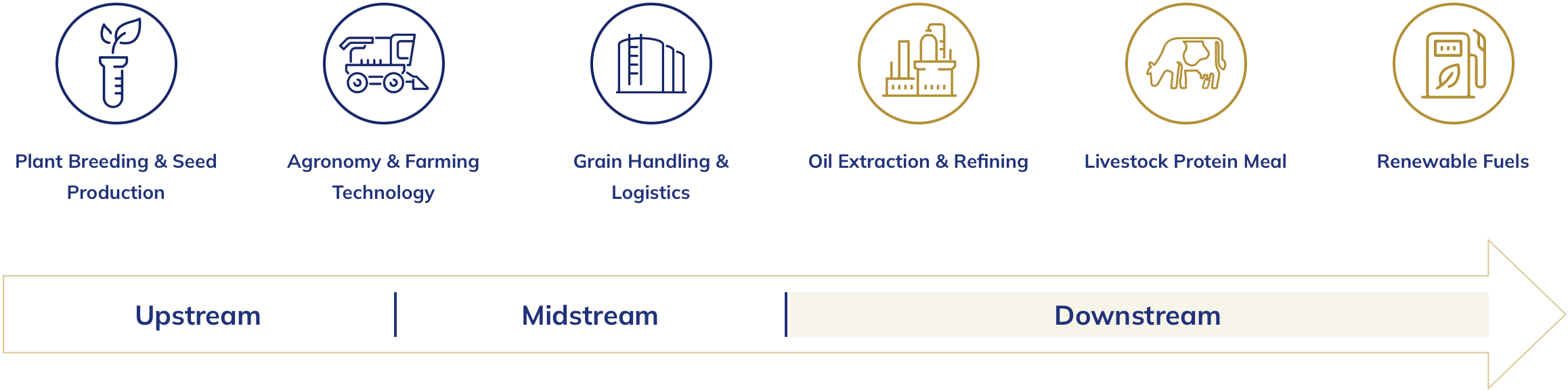
The Company's business is structured into three principal segments:
- Upstream: Focuses on breeding proprietary Camelina varieties and cultivating feedstock through partnerships with farmers globally.
- Midstream: Manages logistics, transportation, storage, and pre-refinement processing of feedstock, linking the Upstream and Downstream operations, often via strategic partners like Louis Dreyfus Company ("LDC").
- Downstream: Centers on the ownership and operation of the Bakersfield Renewable Fuels, LLC ("BKRF") facility in California, which refines Camelina and other biofuel feedstocks into RD and co-products. This segment relies on a supply and offtake agreement with Vitol Americas Corp. ("Vitol") for feedstock supply (like soybean and canola oil) and purchase of finished RD.
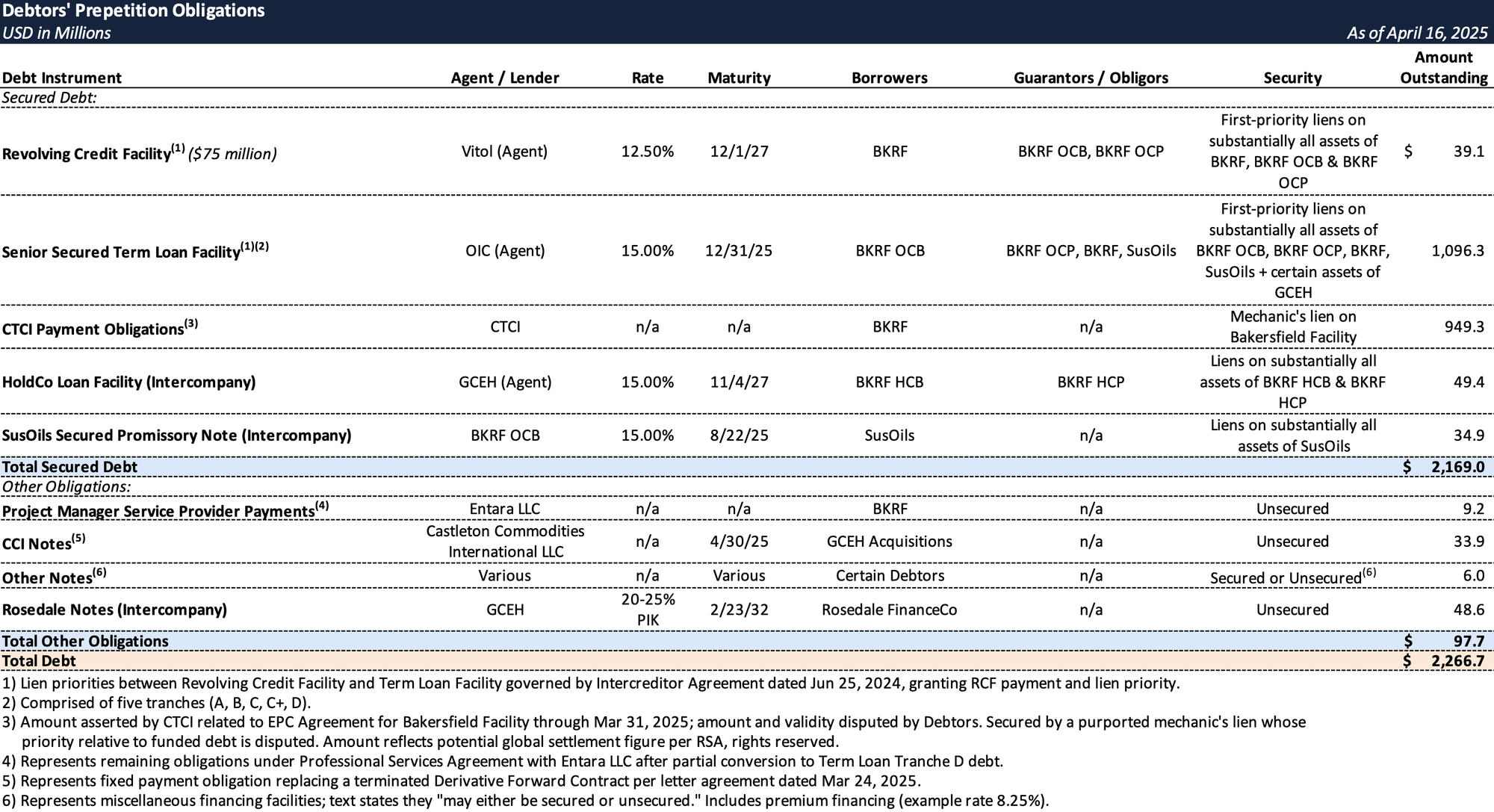
The Debtors filed for Chapter 11 protection on April 16, 2025, in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of Texas. As of the Petition Date, the Debtors reported $1.6 billion in both assets and liabilities.
⁽¹⁾ For a complete list of Debtor entities, see the organizational structure chart below.
Corporate History
Global Clean Energy's focus shifted to the biofuels industry in 2007 when its predecessor, Global Clean Energy Holdings, LLC, relocated from Salt Lake City to Los Angeles. Initially concentrating on cultivating Jatropha seed oil for biodiesel, the Company acquired the trade secrets of this entity and expanded internationally, exploring various plant species for biofuel feedstock.
- Over time, the Company pivoted to focus on Camelina, developing and acquiring what it states is the world's largest portfolio of proprietary Camelina varieties.
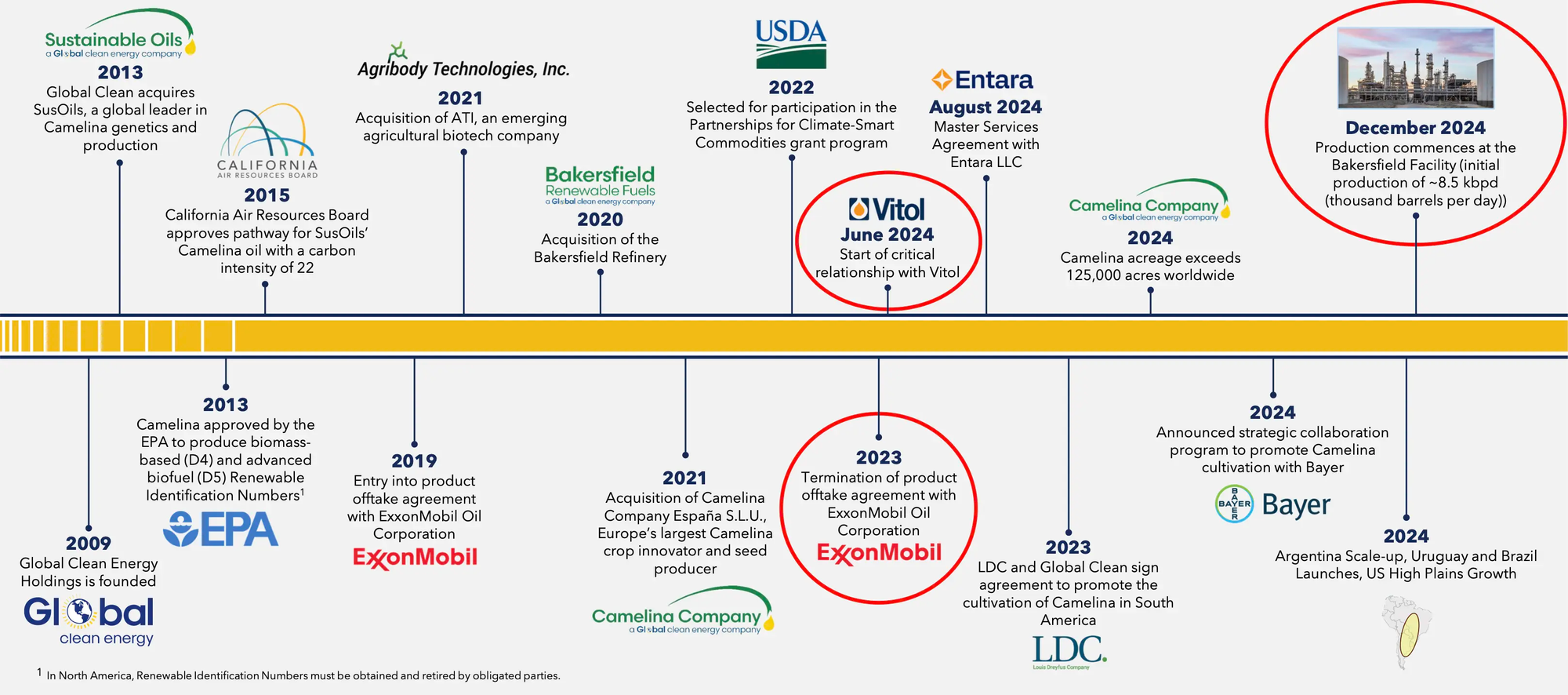
Strategic Acquisitions and Development
- 2013: Acquired Sustainable Oils LLC (predecessor to Debtor Sustainable Oils, Inc. or "SusOils"), a leader in Camelina genetics and production. This coincided with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency ("EPA") approving Camelina under the Renewable Fuel Standard ("RFS") program for biomass-based diesel and advanced biofuel production.
- 2015: Received the first pathway for its Camelina under California's Low Carbon Fuel Standard ("LCFS") program from the California Air Resources Board, enabling its use in producing LCFS-compliant fuels.
- 2020: Acquired the Bakersfield Facility via the purchase of Alon Bakersfield Properties, Inc. (now BKRF) using proceeds from an initial $300 million senior secured term loan facility led by Orion Infrastructure Capital ("OIC"). This move aimed to achieve vertical integration and capitalize on California's LCFS incentives.
- 2020 (December): Debtor Global Clean Energy Holdings, Inc. ("GCEH") common stock began trading under the ticker symbol "GCEH". As of April 11, 2025, the stock traded at $0.37.
- 2021: Further expanded its Upstream capabilities by acquiring:
- Debtor Agribody Technologies, Inc. ("ATI"), an agricultural biotechnology company focused on genomic engineering.
- Entira, Inc., an agriculture business and marketing consulting firm (November).
- Camelina Company España S.L.U. ("CCE"), described as Europe’s largest Camelina crop innovator and seed producer (December).
- 2024 (Fall): Expanded operations into Canada through a non-Debtor subsidiary.
Organizational Structure
Operations Overview
Global Clean Energy operates through its vertically integrated Upstream, Midstream, and Downstream business segments, controlling the process from Camelina seed development to the production and market delivery of renewable fuels.
Upstream Business: Seed Development and Cultivation
- Owns a large portfolio of proprietary Camelina genetics, focusing on breeding varieties with enhanced yield, faster maturity, and tolerance to drought and pests. Debtor ATI holds related patents in genomic engineering.
- Highlights Camelina's advantages: a low-water-use crop suitable for marginal land, capable of being grown in rotation or on fallow land without competing directly with food crops or incurring significant land-use carbon penalties.
- Operates breeding centers in North America, South America, and Europe (via non-Debtor CCE and Global Clean Renewable (Argentina) S.R.L.). Debtor SusOils leads North American efforts. Contractual relationships support seed production globally.
- Partners with growers worldwide to cultivate Camelina:
- Contracted with over 500 growers in 2024.
- Planted acreage nearly doubled from approximately 65,000 acres in 2023 to over 124,000 acres in 2024.
- Expects Camelina cultivation to increase, positioning it as a primary feedstock for the Downstream Business and the broader industry.
Midstream Business: Logistics and Processing
- Coordinates grain handling, logistics, transportation, storage, and pre-refinement processing to move feedstock from farms to the refinery.
- Utilizes a network of logistics providers (including LDC) and grain elevator operators.
- Benefits from the strategic location of the Bakersfield Facility in California, the leading U.S. market for RD consumption. The facility has access to major rail lines, interstate highways, and pipeline networks, facilitating efficient bulk transport from various U.S. growing regions.
- Sells protein-rich Camelina meal, a byproduct of oil extraction, to the animal feed industry. This generated $3.9 million in revenue in 2024 and helps offset Camelina oil production costs.
Downstream Business: Refining and Marketing
- Centered around the Bakersfield Facility, a converted crude oil refinery acquired in 2020 and retooled into a renewable fuels plant.
- Development involved initial work under an EPC contract with Arb, Inc. (terminated after approx. six months) followed by a Turnkey EPC Agreement with CTCI Americas, Inc. ("CTCI") signed in May 2021, targeting completion by January 2022.
- The facility faced delays and cost overruns but became commercially operational in December 2024.
- Primary product is RD (approx. 90% of production), with co-products including renewable propane, naphtha, and butane.
- Produced approximately 450,000 barrels of RD and co-products since launching operations in December 2024.
- Operates under a Supply and Offtake Agreement ("SOA") with Vitol, dated June 25, 2024. Vitol supplies feedstock (e.g., soybean, canola oil) to supplement Camelina supply and purchases all RD produced, along with potentially other outputs like renewable naphtha. Other co-products are sold to various buyers (e.g., Midstream Energy Partners for butane/propane).
- Generated approximately $26 million in revenue in 2024 (primarily in December) and projects $560 million in revenue for 2025.
- Highlights RD advantages: chemically identical to petroleum diesel (100% drop-in replacement), cleaner burning (up to 85% emissions reduction), superior performance compared to traditional biodiesel (no blending needed, better cold weather properties). Camelina-based RD boasts an ultra-low carbon intensity.
- Generates Renewable Identification Numbers (RINs) under the RFS Program, which can be sold to obligated parties (conventional refiners) for compliance purposes.
- Notes potential for future expansion or addition of Sustainable Aviation Fuel ("SAF") production capabilities, leveraging the vertically integrated model and existing infrastructure to tap into growing SAF demand.
Vitol Relationship | Lynchpin of Downstream

Focus on Renewable Diesel

Camelina 101
Prepetition Obligations
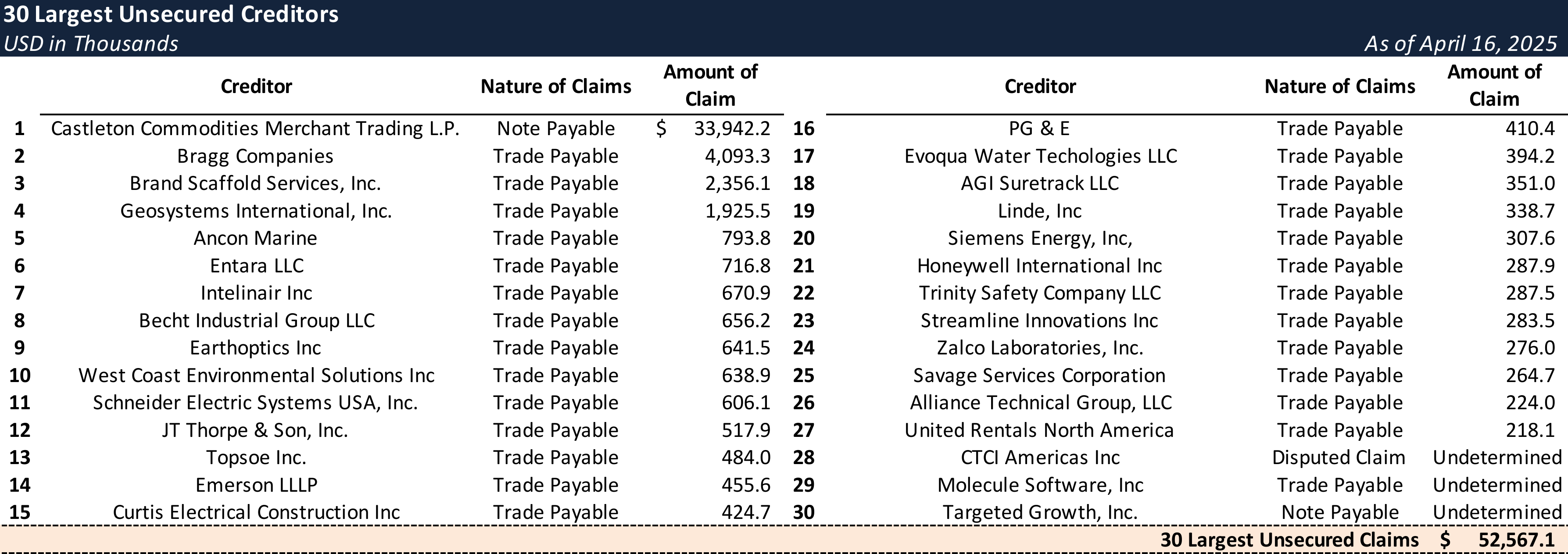
Top Unsecured Claims
Events Leading to Bankruptcy
Bakersfield Facility Construction Issues and Disputes
- Construction of Global Clean Energy's renewable diesel facility in Bakersfield, California, intended to be transformative, was instead beset by significant delays and cost overruns from its early stages.
- Initial setbacks occurred under a prior contractor amid COVID-19 pandemic disruptions (supply chain issues, material shortages, increased freight costs), leading to the termination of the original Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) contract.
- CTCI was subsequently engaged under a new EPC Agreement, initially targeting completion by January 22, 2022, with costs capped at $178 million.
- Ongoing challenges, including licensing, staffing, change orders, and personnel turnover, plagued the project under CTCI, causing further delays and requiring significant Company resource diversion despite the agreement's turnkey nature.
- Efforts to address persistent issues through contract amendments and settlements proved insufficient:
- An January 2023 amendment (EPC Amendment No. 2) increased the guaranteed minimum price to $275 million and set a new substantial completion date of March 31, 2023, which was also missed. It reaffirmed the subordination of any CTCI liens to lender liens.
- Escalating disputes led CTCI to demand mediation and arbitration seeking $550 million in April 2023. Subsequent settlement attempts (Heads of Agreement Oct. 2023, Interim Settlement Agreement Dec. 2023) failed to resolve underlying problems.
- On October 21, 2024, citing incurable defaults, the Company terminated the EPC Agreement with CTCI for cause and exercised its right to complete the remaining work, drawing down a $17.8 million letter of credit provided by CTCI.
- CTCI responded by recording a mechanic's lien for approximately $924.3 million on December 2, 2024, and filed a foreclosure action shortly thereafter (subsequently stayed pending arbitration). A key dispute arose regarding the priority of CTCI's lien relative to the Term Loan Lenders' secured claims, with the Company and the lenders asserting CTCI's claims were contractually subordinated and potentially invalid.
Financial and Operational Fallout from Construction Delays
- The nearly three-year delay in completing the Bakersfield Facility severely hindered the Company's ability to realize its vertically integrated business model and posed an "existential risk."
- The failure to commence operations as anticipated (January 2022) resulted in the loss of significant expected revenue, particularly during a period of high RD prices, severely straining liquidity.
- The operational delays led ExxonMobil Oil Corporation to purportedly terminate its crucial product offtake agreement in early 2023. While disputed and eventually settled in June 2024, this jeopardized vendor relationships and necessitated securing an alternative offtake partner, Vitol, in June 2024.
- To fund escalating construction costs, project delays, operating expenses (including upstream operations), and compensate for the revenue shortfall, the Company became heavily reliant on its Term Loan Lenders.
- Between August 2022 and June 2024, eight amendments to the term loan agreement provided over $382.4 million in incremental funding. Subsequent amendments brought total Term Loan Lender funding to $818.5 million prior to the most recent pre-filing rounds, albeit with significant concessions granted to the lenders.
Market and Regulatory Headwinds
- Global Clean Energy simultaneously faced adverse market conditions and regulatory shifts impacting the renewable fuels sector:
- An oversaturated market for low-emission biofuels led to compressed profit margins for producers.
- The industry experienced rising costs for inputs (natural gas, utilities, transportation, labor) and uncertainty around environmental credits, including declining prices for RINs and California LCFS credits, further depressing margins.
- Significant disruption stemmed from changes in the federal tax credit landscape:
- The volume-based Biodiesel Blenders’ Tax Credit (BTC) expired on December 31, 2024.
- It was replaced by the emissions-based Section 45Z Clean Fuel Production Tax Credit, effective January 1, 2025. Structural differences and lack of implementation guidance for 45Z created significant market trepidation and uncertainty, causing some industry participants to exit projects entirely.
Strategic Alternatives, Advisor Engagement, and Governance
- In response to the mounting operational and financial pressures, the Board initiated a review of strategic and capital structure alternatives in late 2023.
- Lazard was engaged as investment banker in January 2024 to explore options, initially focusing on the Company's Upstream Business (the "Upstream Capital Process").
- As liquidity tightened further in the fall of 2024, the Company retained Kirkland & Ellis as legal counsel and Alvarez & Marsal as financial advisor to assist with liquidity management, lender engagement, and a broader review of alternatives.
- The Board proactively addressed governance, appointing experienced restructuring professional Todd Arden as an independent director in December 2024 and establishing a Special Committee (comprising Arden and existing independent director Susan Anhalt) to evaluate restructuring alternatives and address potential conflicts.
Prepetition Marketing Efforts Yield No Actionable Bids
- Despite extensive marketing efforts led by Lazard, no viable out-of-court transaction emerged:
- The Upstream Capital Process, launched in early 2024, involved outreach to over 100 parties and yielded two initial non-binding IOIs but did not progress to a transaction.
- In December 2024, the process was expanded to market all or substantially all of the Company's assets, contacting over 75 parties.
- Notwithstanding these efforts, no actionable IOIs or bids were received by the February 24, 2025 deadline, although diligence continued with certain parties.
Stakeholder Negotiations and Path to Chapter 11
- With marketing efforts unsuccessful, Global Clean Energy focused on negotiating a comprehensive resolution with its key stakeholders through the fall of 2024 and into 2025.
- Intensive discussions commenced with an ad hoc group holding ~96% of the Term Loans (the "Ad Hoc Term Lender Group") and their advisors.
- Negotiations also began with CTCI and its advisors to seek a global settlement of the construction disputes, including the critical lien priority issue.
- The Company engaged with Vitol, its revolving credit facility lender and essential supply/offtake partner, to align on complementary restructuring terms.
- Despite the ongoing disputes and risks, the Term Loan Lenders provided crucial interim liquidity, funding over $75 million through six additional credit agreement amendments between December 2024 and April 2025 (approximately half in the two months pre-petition).
- It became evident that an in-court restructuring was necessary, and potential financing parties (including the Ad Hoc Term Lender Group, Vitol, and CTCI) required the protections of DIP financing. Interest from third-party DIP sources was minimal.
- Months of hard-fought, arm's-length negotiations culminated in an agreement in principle among Global Clean Energy and the key Consenting Stakeholders (Ad Hoc Term Lender Group, CTCI, Vitol) in late March 2025, forming the basis for the Restructuring Support Agreement.
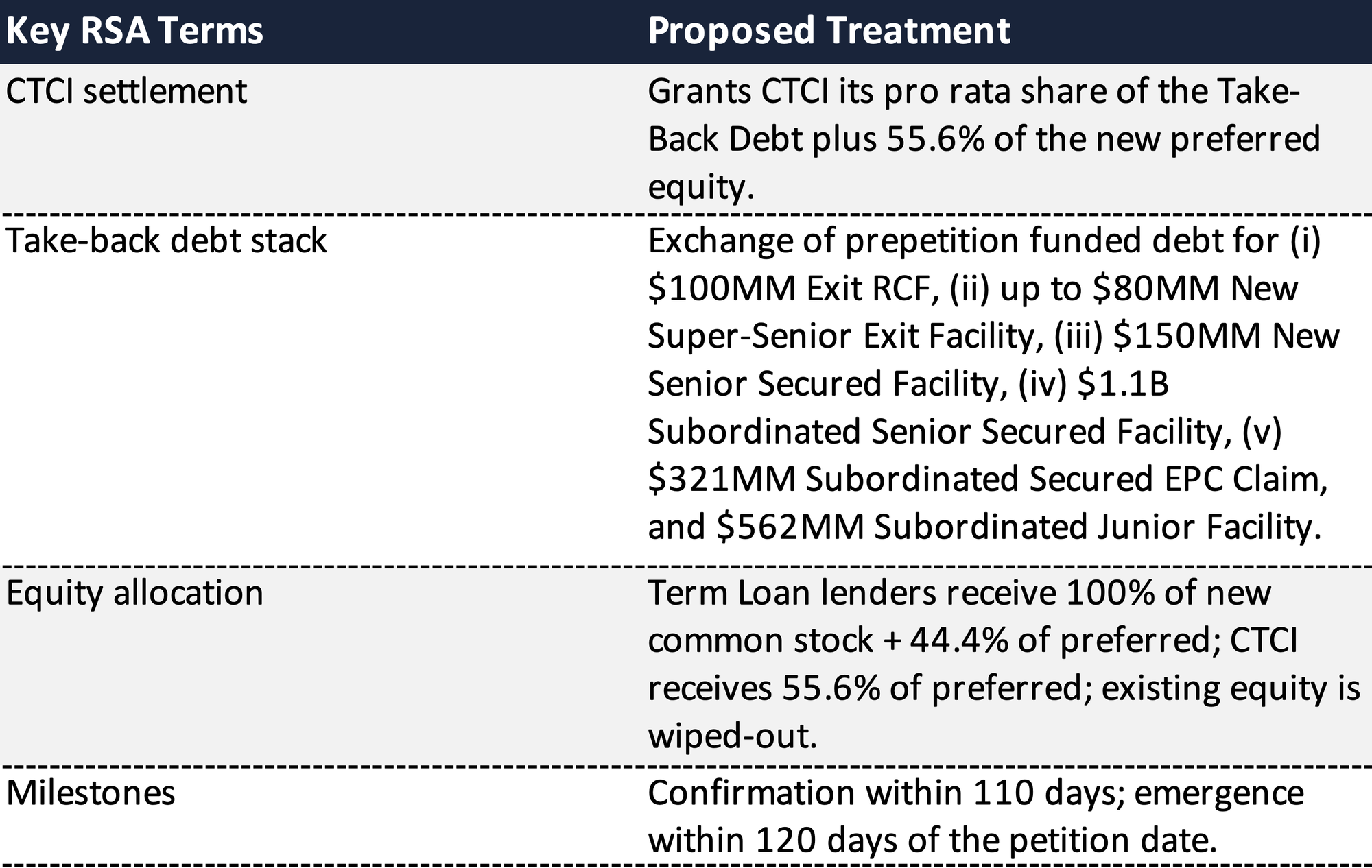
Restructuring Support Agreement (RSA)
The Debtors finalized the RSA with Consenting Stakeholders immediately prior to filing, memorializing a comprehensive restructuring plan filed contemporaneously. Key elements include:
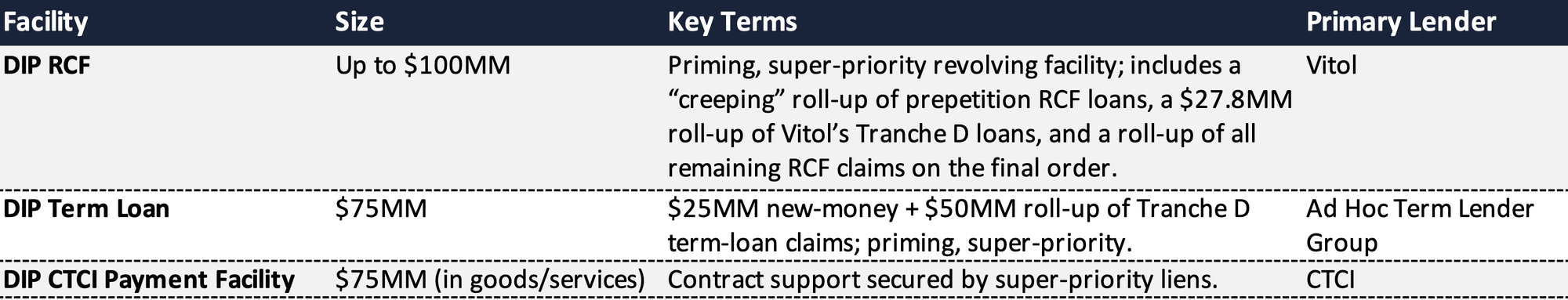
DIP Financing
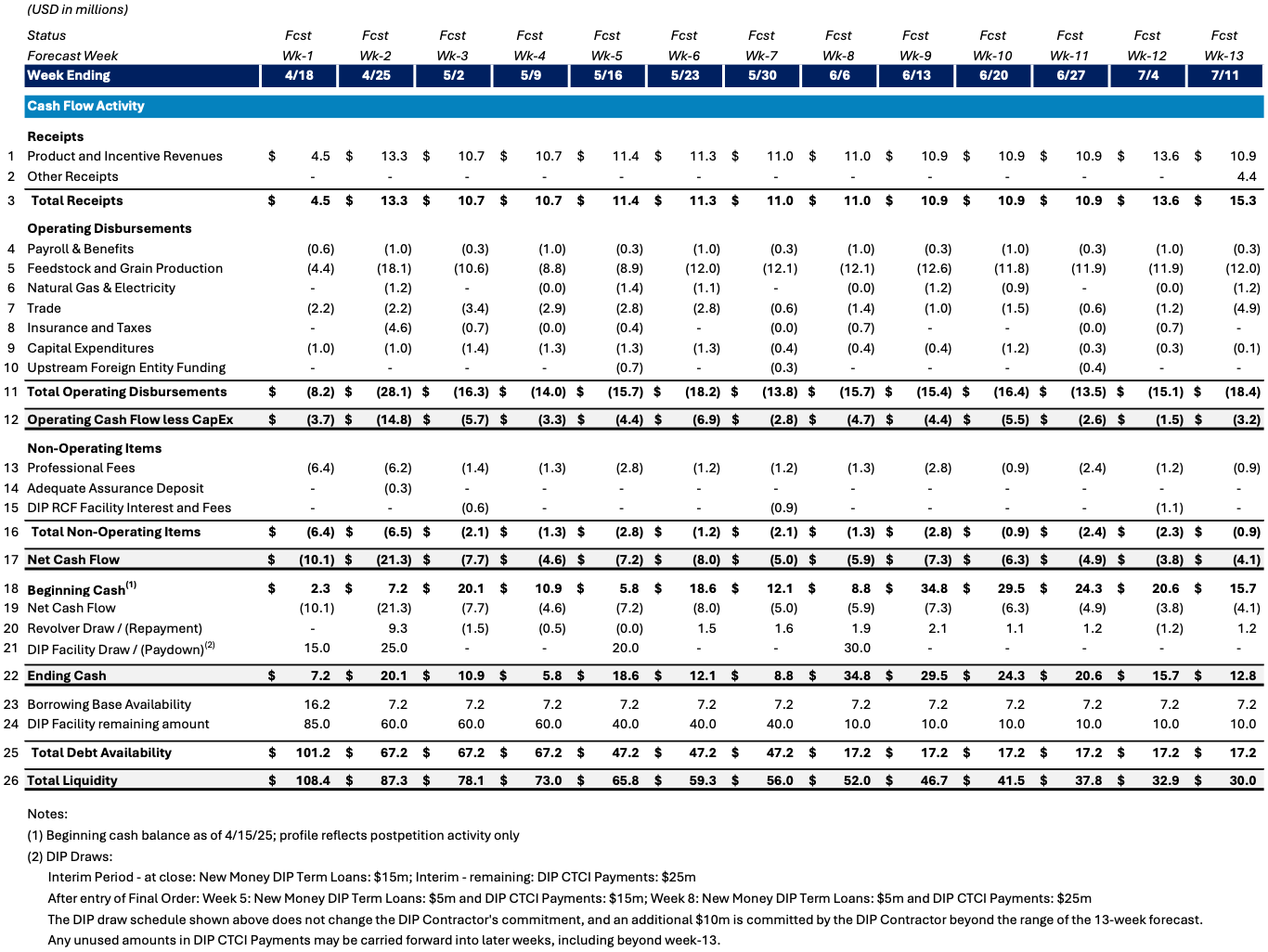
Initial Budget
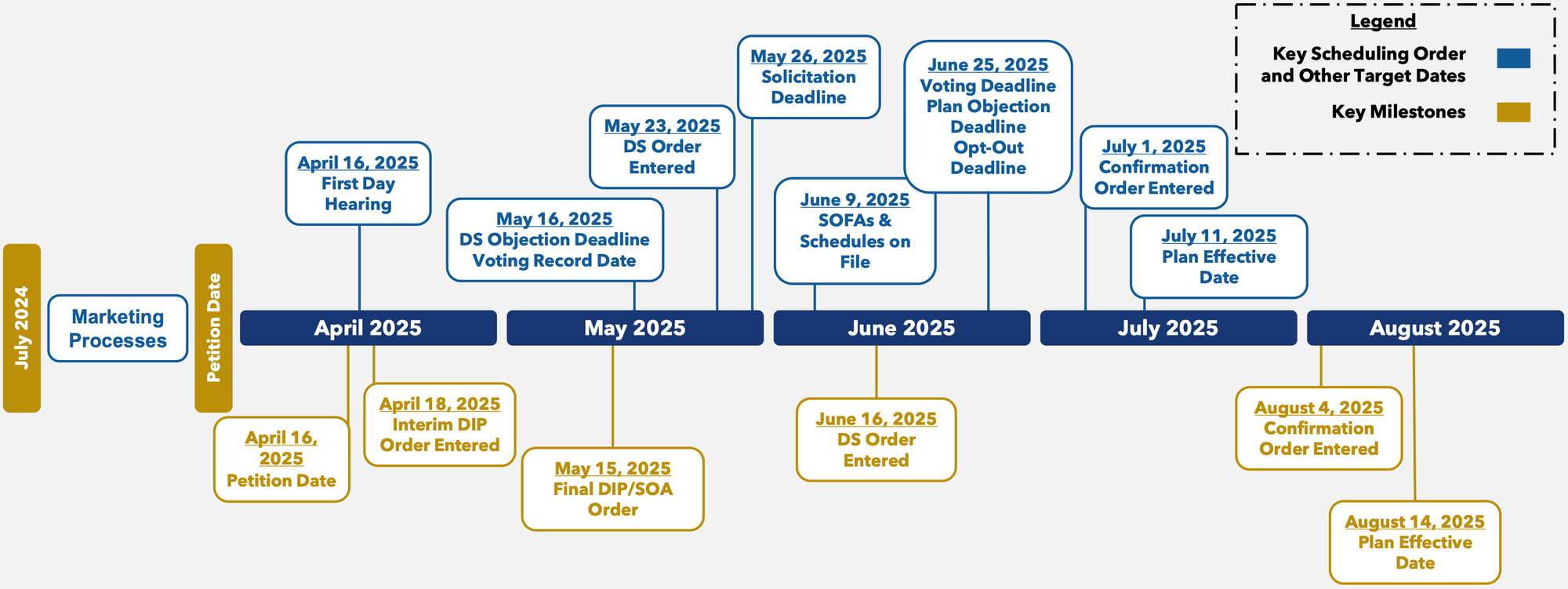
Proposed Case Timeline
Key Parties

Stay informed on every Chapter 11 bankruptcy case with liabilities exceeding $10 million. Subscribe for free to have our coverage delivered directly to your inbox, and explore our full archive of past summaries.
If you're already a subscriber and would like to receive timely filing alerts, please reach out and we'll add you to the distribution list.



