Case Summary: Mitel Chapter 11
Mitel has filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy to cut roughly $1.15 billion in debt under a prepackaged plan amid competitive pressure from cloud-based rivals.

Business Description
MLN US HoldCo LLC, along with its Debtor⁽¹⁾ and non-Debtor affiliates (collectively, "Mitel" or the "Company"), is a leading global provider of telecommunications solutions tailored for small, midsize, and enterprise-level businesses.
Mitel's product suite spans hardware, software subscriptions, and professional support services, designed to facilitate seamless connectivity and collaboration for over 65 million users across 146 countries.
- In FY24, the Company generated approximately $426 million from Software & Subscription Products, $276 million from Professional & Support Services, and $205 million from Hardware Products.
- Mitel derives approximately 88% of its global revenue through an extensive network of partners.
As of the Petition Date, Mitel employs roughly 4,284 individuals worldwide, including approximately 760 employees in the U.S. and Canada, supplemented by 57 independent contractors and 162 temporary staff.
The Debtors filed for Chapter 11 protection on Mar. 9 in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of Texas⁽²⁾. As of the Petition Date, the Debtors reported $1 billion to $10 billion in both assets and liabilities.
⁽¹⁾ See the Chapter 11 Debtors table below for a full list of Debtors. ⁽²⁾ On March 10, Debtor Mitel Networks Corporation ("MNC") filed an application under Canada’s Companies’ Creditors Arrangement Act (CCAA) seeking recognition of the U.S. proceedings and an interim stay of proceedings in Canada, with Mitel Networks Corporation acting as Foreign Representative.
Corporate History
Mitel was founded in Ottawa, Canada, in 1973 by Michael Cowpland and Terry Matthews, initially developing tone receiver technology and small-scale business telephone systems (PBX). The Company rapidly became a dominant North American PBX provider.
- Facing financial pressures, Mitel sold a controlling 51% stake to British Telecom in 1985 but later completed a management-led buyout with Schroeder Ventures in 1992, redirecting its focus towards integrating telephony with computing.
- In 2001, co-founder Terry Matthews reacquired the Company's communications division, rebranding as Mitel Networks, and pivoted toward Voice-over-IP technology.
Key Acquisitions and Expansion
- Mitel’s strategic growth was propelled by acquisitions of Inter-Tel (2007), Aastra Technologies (2014), ShoreTel (2017), and Unify (2023), significantly enhancing its global footprint and cloud capabilities.
- In 2010, the Company listed publicly on Nasdaq but returned to private ownership in a $2 billion leveraged buyout by Searchlight Capital Partners in 2018.
Financial Structure Post-Acquisition
- The acquisition was financed through Legacy Senior Term Loans ($1.12 billion), Legacy Junior Term Loans ($260 million), and a $100 million revolving credit facility, which was later reduced to $90 million and subsequently further reduced to $65 million in November 2022.
- Mitel subsequently pursued strategic partnerships, notably with RingCentral and Five9 in 2021, to bolster its cloud-based offerings and competitive edge.
Organizational Chart
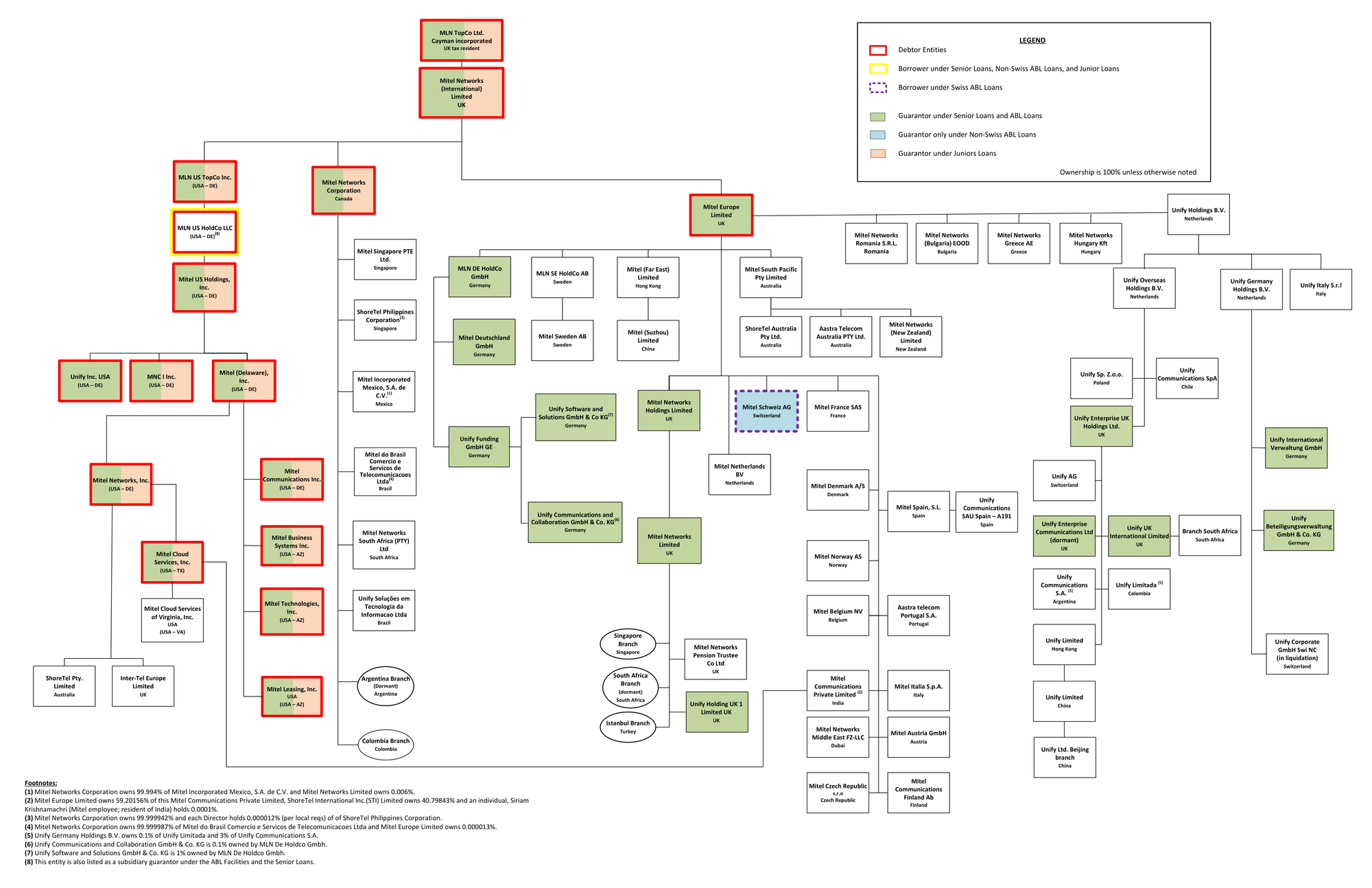
- Following the Searchlight Acquisition, Mitel Networks amalgamated under Canadian law, forming Mitel Networks Corporation ("MNC"), the sole Canadian Debtor entity holding substantial intellectual property, including over 900 patents and 166 trademarks.
- Operations are primarily conducted through subsidiaries in the United States, Germany, the United Kingdom, and Canada under the ownership of MLN TopCo Ltd., a Cayman Islands holding company.
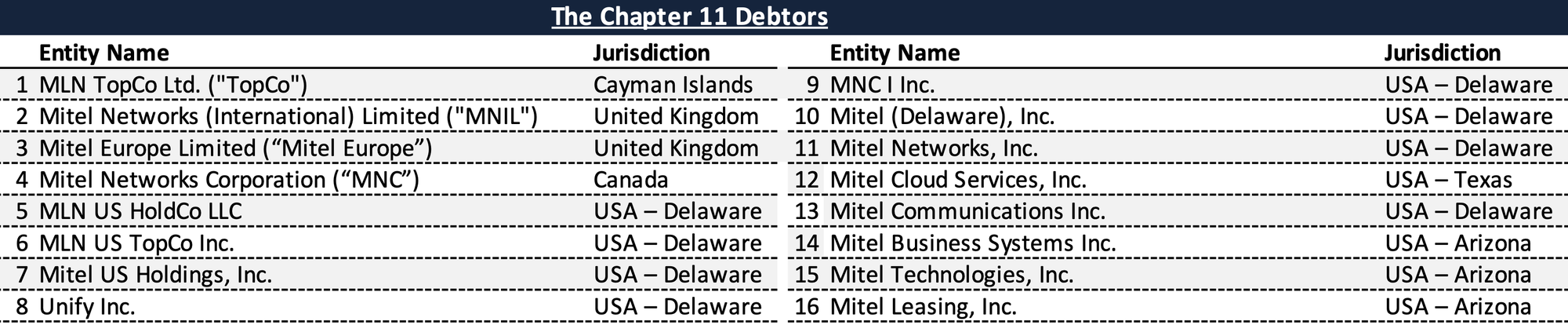
The Chapter 11 Debtors
Operations Overview
Mitel operates globally through three primary geographic markets—Americas, EMEA, and Asia-Pacific—with notable market strength in North America and Europe. Historically known for its on-premise PBX systems, Mitel now emphasizes hybrid-cloud communication solutions through strategic alliances with RingCentral and Five9.
Revenue Segments
- Software & Subscription Products (43% of 2024 revenue): Unified Communications and Contact Center solutions provided via on-premise deployments (MiVoice Business and MiVoice Office systems), cloud platforms (previously MiCloud, now serviced by RingCentral), and hybrid deployments blending infrastructure.
- Professional & Support Services (28%): Consultation, integration, migration, training, and managed support, leveraging a global partner network of over 6,000 channel and distribution partners. Acquisitions such as PrairieFyre and ShoreTel have further enhanced Mitel's professional service capabilities.
- Hardware Products (20%): IP desk phones, conferencing hardware, attendant consoles, and wireless solutions. Manufacturing has been outsourced since 2002 to contract manufacturers, optimizing supply chain flexibility and integration with third-party solutions (e.g., Microsoft and Zoom).
Mitel's 2023 acquisition of Unify significantly expanded its European presence, solidifying the Company's position as the world's second-largest unified communications provider by active users. The Company's integrated approach, spanning software, services, and hardware, uniquely positions Mitel amidst a competitive landscape increasingly dominated by cloud-native competitors.
Prepetition Obligations
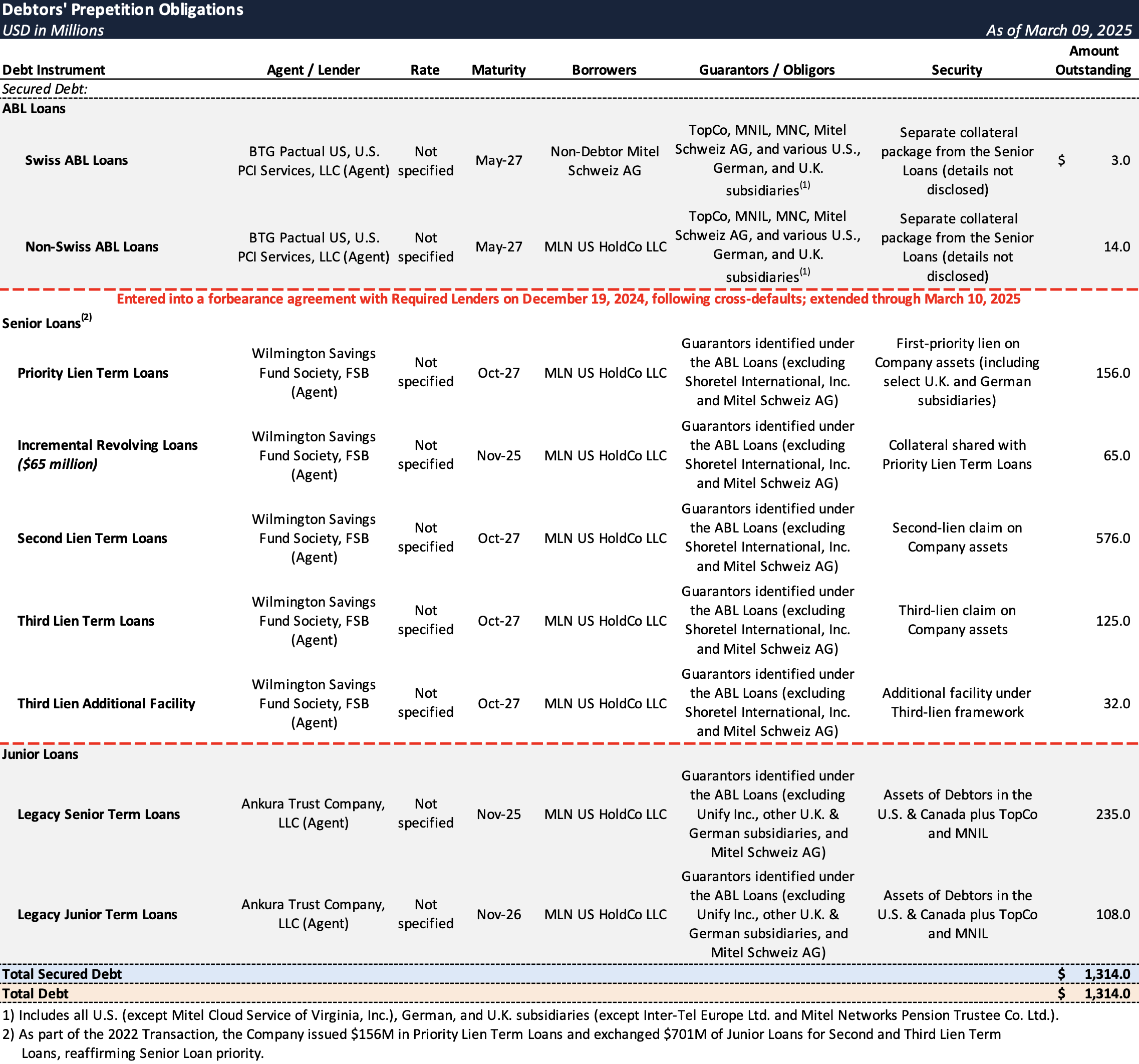
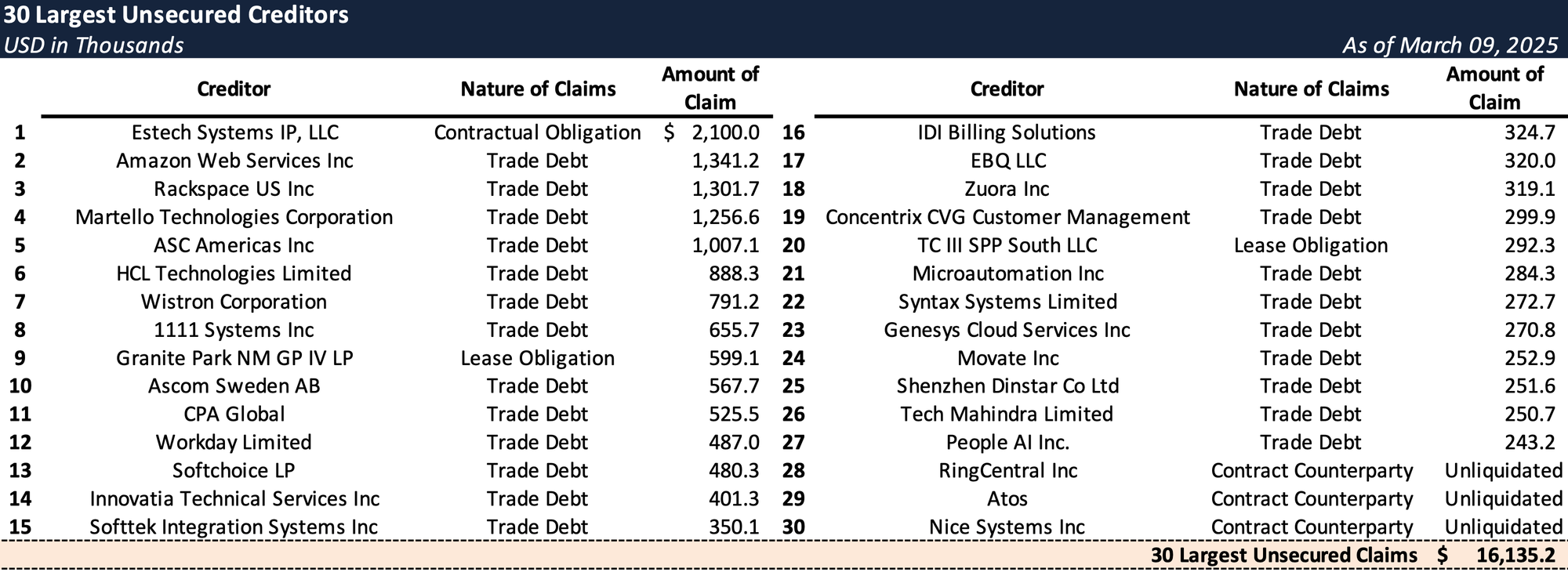
Top Unsecured Claims
Events Leading to Bankruptcy
Industry and Macroeconomic Pressures
- Mitel faced substantial financial strain due to rapid industry shifts, intensified competition, and challenging macroeconomic conditions.
- Cloud-native providers such as Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Cisco Webex disrupted traditional markets, pushing Mitel to transition rapidly to hybrid-cloud offerings.
- The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the decline of demand for traditional PBX hardware, compressing margins and adding operational complexity.
- Inflation, rising interest rates, and supply-chain disruptions compounded liquidity constraints, particularly impacting Mitel’s hardware operations.
Strategic Initiatives and Liquidity Pressures
- To stabilize finances, Mitel pursued several strategic initiatives:
- In 2021, the Company entered a critical partnership with RingCentral, selling its CloudLink platform for approximately $650 million and redirecting UCaaS customers to RingCentral’s cloud platform; however, slower-than-expected migrations limited immediate benefits.
- Partnerships with Five9 in 2021 and the acquisition of Unify in 2023 enhanced hybrid-cloud capabilities but required significant investment, further straining liquidity.
- Persistent liquidity shortfalls led Mitel to execute a $701 million recapitalization in 2022 (the "2022 Transaction") with a group of Senior Lenders representing a majority of existing Junior Loan holders, but slower-than-expected returns and significant integration costs from Unify heightened liquidity pressures.
- The transaction included issuing new secured debt to these Senior Lenders, elevating their obligations to a first-priority position ahead of the Junior Loans.
- Litigation challenging the 2022 Transaction added to financial uncertainty, despite eventual dismissal by the New York Appellate Division in December 2024.
Path to Chapter 11 Filing
- Despite renegotiations with RingCentral, divestment of its UCaaS business, and a new partnership with Zoom Communications, Mitel concluded by November 2024 that refinancing existing debts was untenable.
- In December 2024, a forbearance agreement provided temporary relief but activated cross-defaults under senior debt agreements, compelling negotiations with stakeholders—including the Ad Hoc Group of Senior Lenders and Searchlight.
- After rigorous negotiations, an agreement-in-principle was reached, formalized in the Restructuring Support Agreement ("RSA") on March 9, 2025, garnering robust stakeholder support:
- The RSA was endorsed by 100% of ABL Loan Claims, 72.1% of Priority Lien Claims, and 81.1% of Non-Priority Lien Term Loan Deficiency Claims.
- The prepackaged Chapter 11 restructuring plan aims to deleverage the Company's balance sheet by $1.15 billion, reducing annual cash interest expenses by approximately $135 million.
- To support ongoing operations during restructuring, Mitel secured $60 million in DIP financing and arranged an additional $64.5 million in exit financing to maintain liquidity upon emergence.
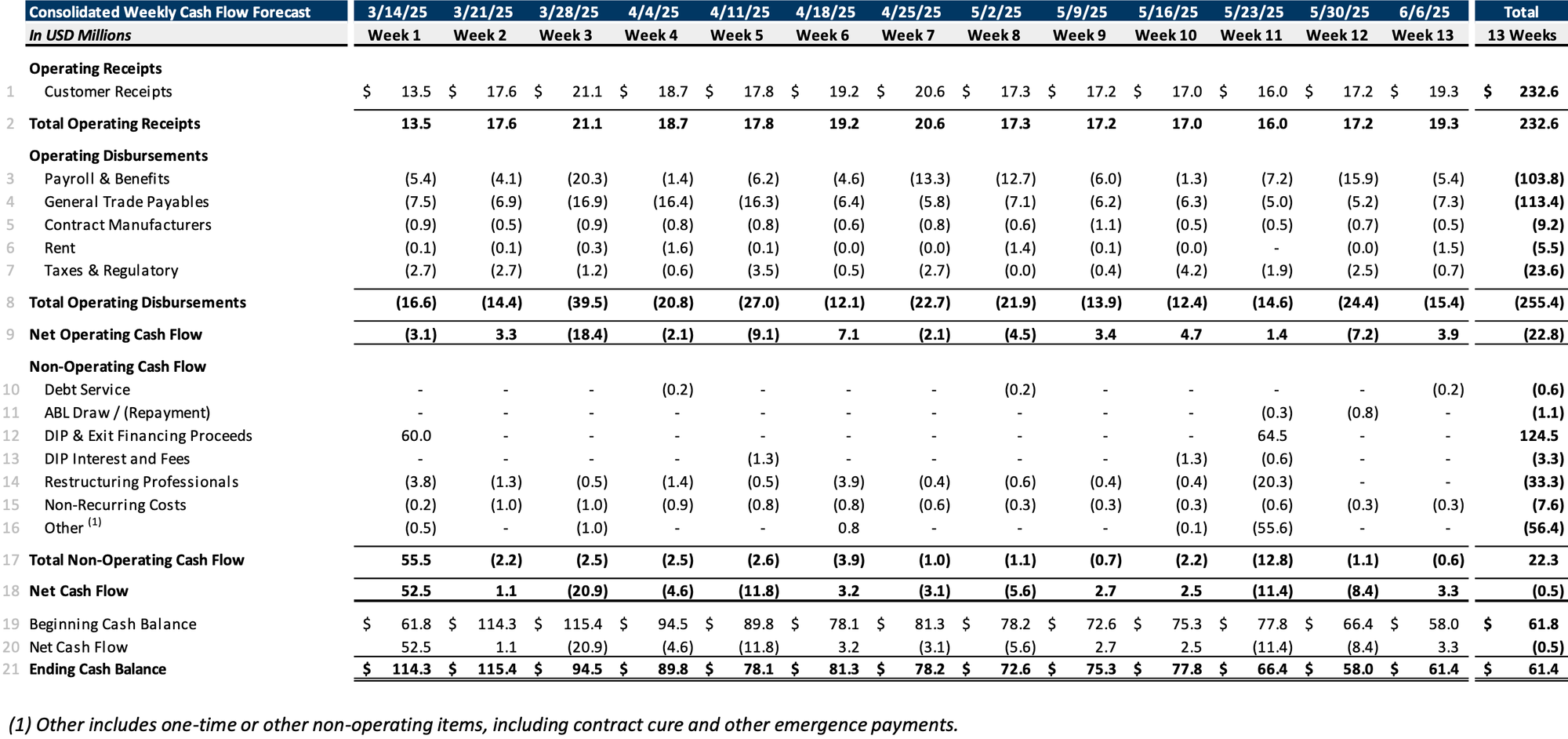
Initial Budget
Stay informed on every Chapter 11 bankruptcy case with liabilities exceeding $10 million. Subscribe for free to have our coverage delivered directly to your inbox, and explore our full archive of past summaries.
If you're already a subscriber and would like to receive timely filing alerts, please reach out and we'll add you to the distribution list.



