Case Summary: On The Border Mexican Grill & Cantina Chapter 11
On The Border has filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy, citing macroeconomic challenges, labor shortages, and costly leases from underperforming locations, with plans to sell assets.

Business Description
OTB Holding LLC (dba On The Border Mexican Grill & Cantina), along with its Debtor⁽¹⁾ and non-Debtor affiliates, (collectively, “On The Border” or the "Company"), operates as a full-service Tex-Mex casual dining chain.
- The Company is best known for its mesquite-grilled fajitas, signature margaritas, and endless chips & salsa, delivering a bar-centric dining experience with an extensive Tex-Mex menu.
- The brand emphasizes a high-energy, “fiesta” atmosphere, leveraging themed events, loyalty programs, and value-driven promotions to drive customer engagement.
As of the Petition Date, On The Border operated over 80 locations globally, including 60 leased corporate-owned restaurants across 18 U.S. states and 20 franchised locations in the U.S. and South Korea.
- Franchise royalties generated approximately $1.8 million in FY 2024.
The Debtors filed for Chapter 11 protection on Mar. 4 in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Northern District of Georgia. As of the Petition Date, the Debtors reported $10 million to $50 million in both assets and liabilities.
⁽¹⁾ The Debtors are identified in the Organizational Chart below.
Corporate History
On The Border was founded in October 1982 in Dallas, TX, as "On The Border South Texas Café." In 1994, Brinker International acquired the Company, accelerating its growth and opening the first franchised location soon thereafter.
- By 2001, On The Border had surpassed 100 domestic restaurant locations and, in 2007, extended its reach into South Korea through franchised units.
Ownership Transitions
- In 2010, Brinker International sold On The Border—including its 160 cantinas at the time—to Golden Gate Capital.
- Golden Gate Capital then transferred ownership to Border Holdings LLC, an affiliate of Argonne Capital Group, in 2014.
- In 2020, Utz Brand acquired the rights to produce and distribute On The Border™ branded chips and dips.
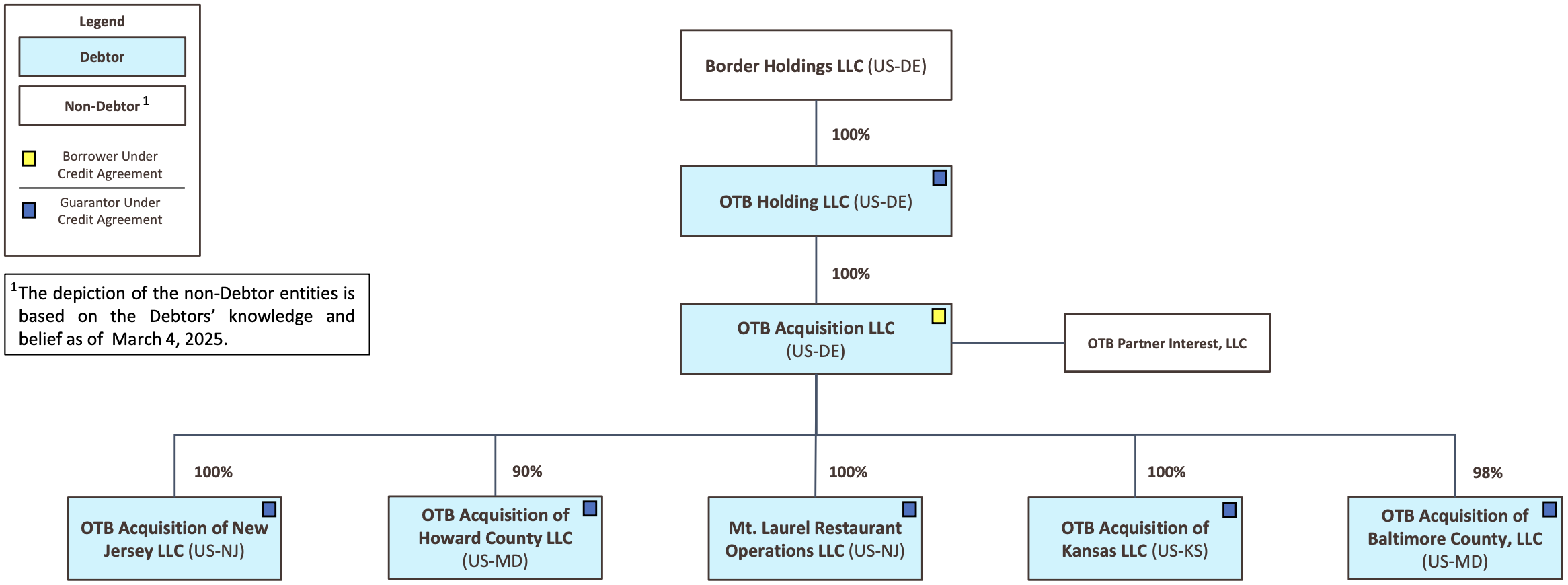
Organizational Chart
The corporate structure consists of multiple subsidiaries under Debtor OTB Holding LLC, with all operating assets owned by OTB Acquisition LLC.
Operations Overview
On The Border follows a full-service restaurant model, featuring from-scratch cooking and a dedicated waitstaff. Its culinary approach emphasizes fresh-pressed tortillas, house-made salsas, and mesquite-grilled meats to maintain consistency across locations.
Franchise Structure & Restaurant Formats
- On The Border operates approximately 60 leased corporate-owned and 20 franchised locations, with franchise growth concentrated in international markets.
- The Company’s restaurant design incorporates Tex-Mex architectural elements, including stucco exteriors, colorful accents, and terracotta roof tiles.
- Most locations feature a dining area, a separate bar/cantina space, and an outdoor patio.
- In 2021, the Company introduced a redesigned prototype in Alpharetta, GA, modernizing its concept while maintaining its brand identity.
- To support evolving consumer preferences, On The Border has also explored alternative formats, such as ghost kitchens, to strengthen its off-premise sales and delivery operations.

Technology & Efficiency Initiatives
- As part of its digital transformation strategy, On The Border launched the “Queso Club” loyalty program, introduced a mobile ordering app, and revamped its website to enhance the guest experience.
- Operational efficiency improvements include expanded third-party delivery partnerships with DoorDash and Uber Eats, alongside upgrades to POS and kitchen management systems designed to optimize order flow and restaurant performance.
Workforce & Support Infrastructure
- As of the Petition Date, On The Border employed approximately 2,800 staff members, including 375 full-time hourly workers, 2,210 part-time hourly employees, and 216 full-time salaried personnel.
- The Company does not operate under union agreements or collective bargaining arrangements.
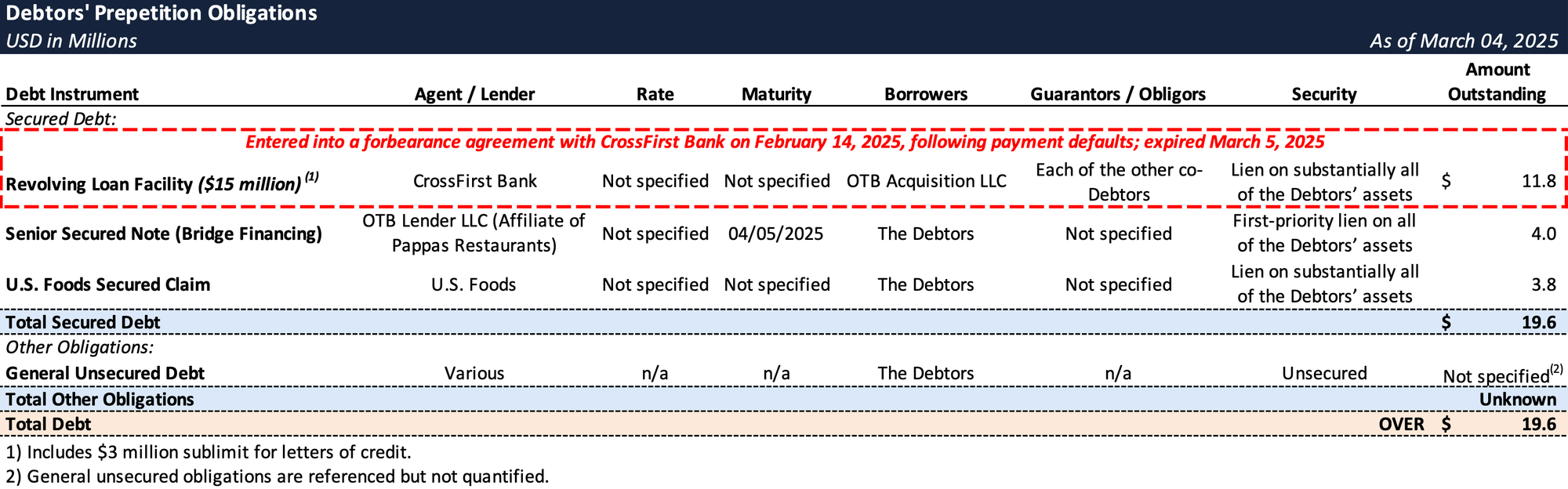
Prepetition Obligations
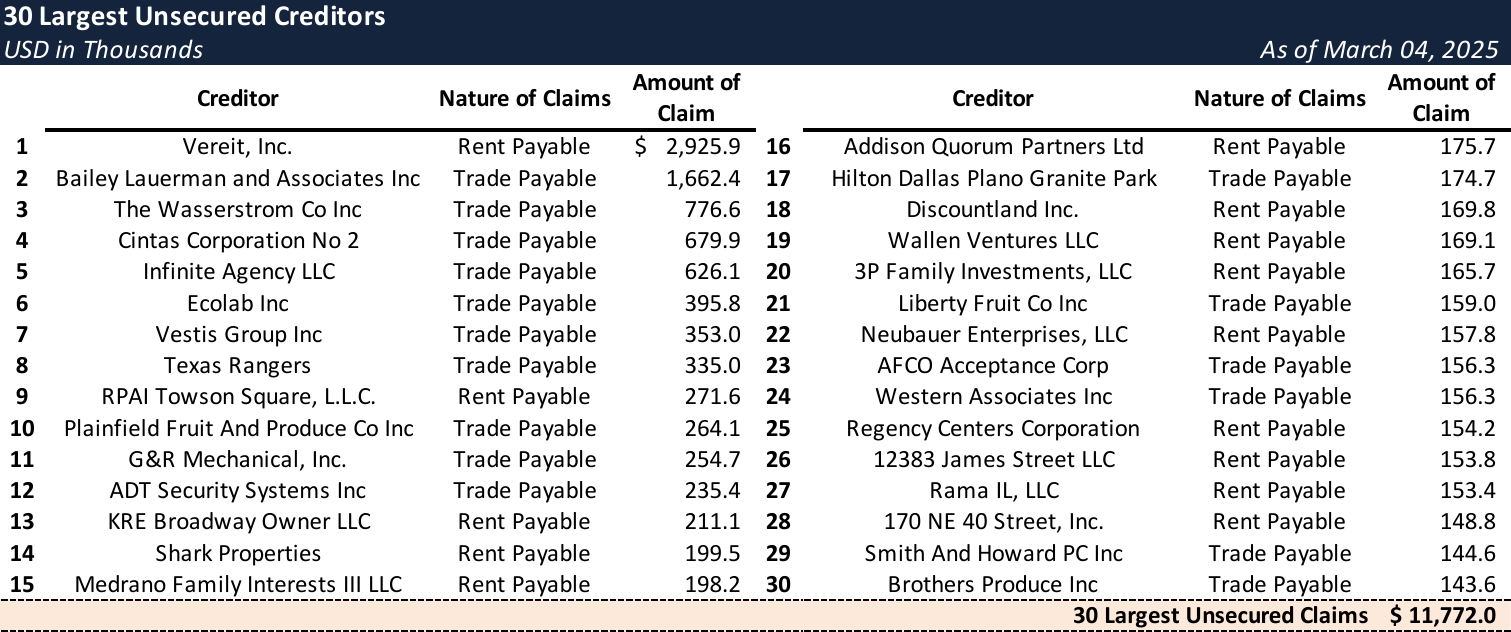
Top Unsecured Claims
Events Leading to Bankruptcy
Macroeconomic and Labor Pressures
- On The Border’s performance has been significantly impacted by challenging macroeconomic conditions and consumer sensitivity to dining out.
- Inflationary pressures have driven restaurant menu prices higher than grocery and other consumer goods, reducing consumer willingness to eat out.
- Labor costs have outpaced price increases, and more than half of U.S. states raised minimum wages in 2024, further constraining margins.
- The Company has struggled to recruit and retain a sufficient workforce, exacerbating operational inefficiencies.
Lease Burdens and Underperforming Restaurants
- As of the Petition Date, the Company held 113 active restaurant leases, many tied to non-operational or underperforming locations.
- In 2024, the Company spent approximately $25.3 million on lease obligations, with approximately $11.9 million attributable to underperforming stores.
- High rent costs at nonperforming sites created significant liquidity strains, prompting the Company to pursue lease rejections for closed locations.
- On The Border closed and vacated 40 stores on or around February 24, 2025, seeking to reduce its footprint and redeploy available staff where possible.
- These closures targeted restaurants deemed too costly due to rent burdens or insufficient financial performance.
Liquidity Constraints and Creditor Actions
- In the months leading up to the bankruptcy filing, the Company’s liquidity rapidly deteriorated, forcing it to suspend vendor and rent payments.
- Vendors and landlords cut off services, withheld goods, and exercised set-off rights, resulting in additional store losses and severe operational challenges.
- After exploring multiple alternatives to raise capital, the Company’s managers concluded that a Chapter 11 filing was the most viable path to preserve and maximize value.
- Persistent labor shortages, declining revenue, and enforcement actions contributed to the decision to pursue a strategic asset sale under section 363 of the Bankruptcy Code.
Marketing and Sale Process
- In January 2025, the Company engaged Hilco Corporate Finance, LLC ("Hilco") to market its assets for a possible going-concern sale or another value-maximizing transaction.
- Hilco contacted 273 potential strategic and financial bidders, leading to active discussions and confidentiality agreements with 31 parties.
Stalking Horse Agreement & Bidding Procedures
- On March 7, 2025, the Company entered into an Asset Purchase Agreement with OTB Hospitality, LLC (affiliate of Pappas Restaurants) as the Stalking Horse Purchaser.
- The Stalking Horse Bid consists of:
- A credit bid for the full amount of the Secured Note Obligations and DIP Obligations.
- Potential for additional cash consideration.
- The bidding procedures allow for higher and better bids and include:
- A bid deadline of May 1, 2025.
- An auction scheduled for May 6, 2025, if qualified bids are received.
- A minimum overbid increment of $150,000 beyond the $600,000 breakup fee and $350,000 expense reimbursementfor the Stalking Horse Bidder.
- A sale hearing scheduled no later than May 10, 2025.
DIP Financing Structure
- The Company secured $14 million in DIP financing under an Interim DIP Order entered on March 7, 2025, with OTB Lender, LLC as the DIP lender. The financing includes:
- $7.5 million in new money DIP Loans.
- A $4 million roll-up of the Secured Note.
- An additional $2.5 million in new money DIP loans contingent upon entry of the Final DIP Order.
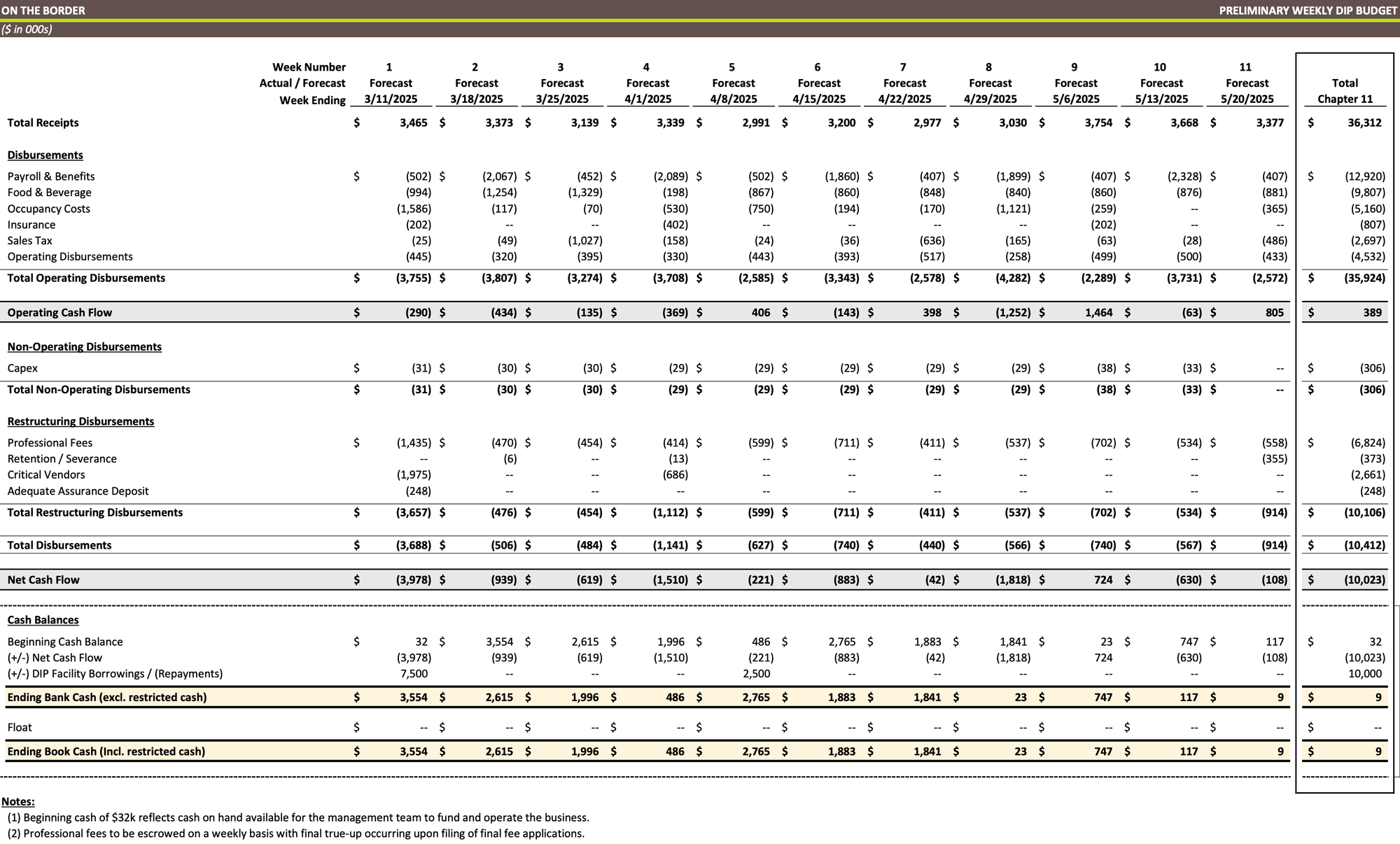
Preliminary Weekly DIP Budget
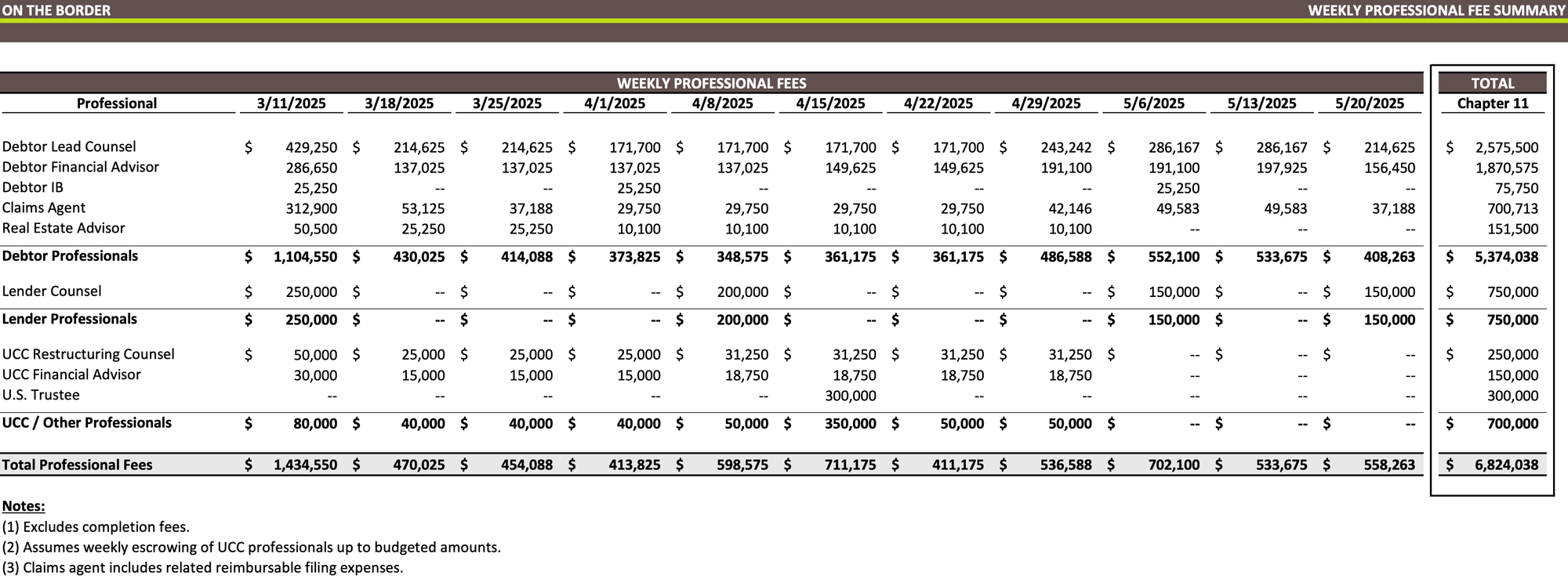
Weekly Professional Fee Summary
Stay informed on every Chapter 11 bankruptcy case with liabilities exceeding $10 million. Subscribe for free to have our coverage delivered directly to your inbox, and explore our full archive of past summaries.
If you’re already a subscriber and would like to receive timely filing alerts, please reach out and we’ll add you to the distribution list.



